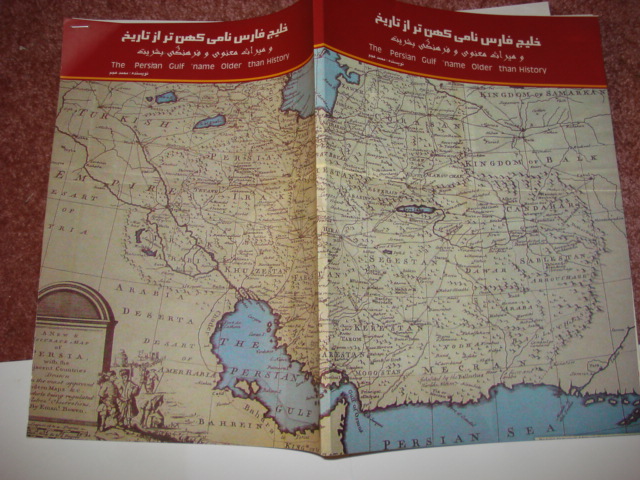
Introducing a Book and Atlas
Documents on the Persian Gulf’s name the eternal heritage of ancient time . part 2
in the picture Dr.Ali Larijani speaker of parement of Iran and some members of the parlement also deputies of MoFA Iran and india
Documents on the Persian Gulf’s name the eternal heritage of ancient time . part 2
Introducing the bookDocuments on the Persian Gulf’s name the eternal heritage of ancient time” is a book and atlas written and compiled by Dr. M. Ajam. published on 2004. A second edition was published under the supervision of Dr. Pirouz Mojtahedzadeh and Dr.M. Ganji in 2009. The book was chosen as a candidate to receive prize of the best book of the year 2010 in Iran and was announced and ranked by the books authority of Iran among the best books in the last 50 years on the subject of ” Persian Gulf issues” in Persian language.
** Awards**
At the eleventh International Festival of Iran's Best Researchs and Researchers of 2010, **this book received the Gold Coin of Excellence Award presented by the Vice President. This book has received many other awards and numerous other letters of appreciation among them a letter from former president Hashemi Rafsanjani.
And a newer version of it was released in 2009. The contents of this book have been repeatedly published in the Persian media. According to the recommendations of this book, * the Persian Gulf National Day* was registered by the Iranian government in 2005.
Part of the book was presented to the United Nations as a national report and published on its geographical site.
a summary of the book had been published on the UN website in 2006 under the title
:It also can be read in this address
part of the book also had been included in the book “Persian Gulf by Javad Norozi and translated and published into 10 languages : Persian, Arabic, English, French, German, Italian, Spanish, Russian, Chinese and Urdu ,also a famous documentary film titled Persian Gulf Name in the Course of History by Orod Atarpour has been produced and broadcasted in IRIB TV and Press TV mainly based on the document of this book.
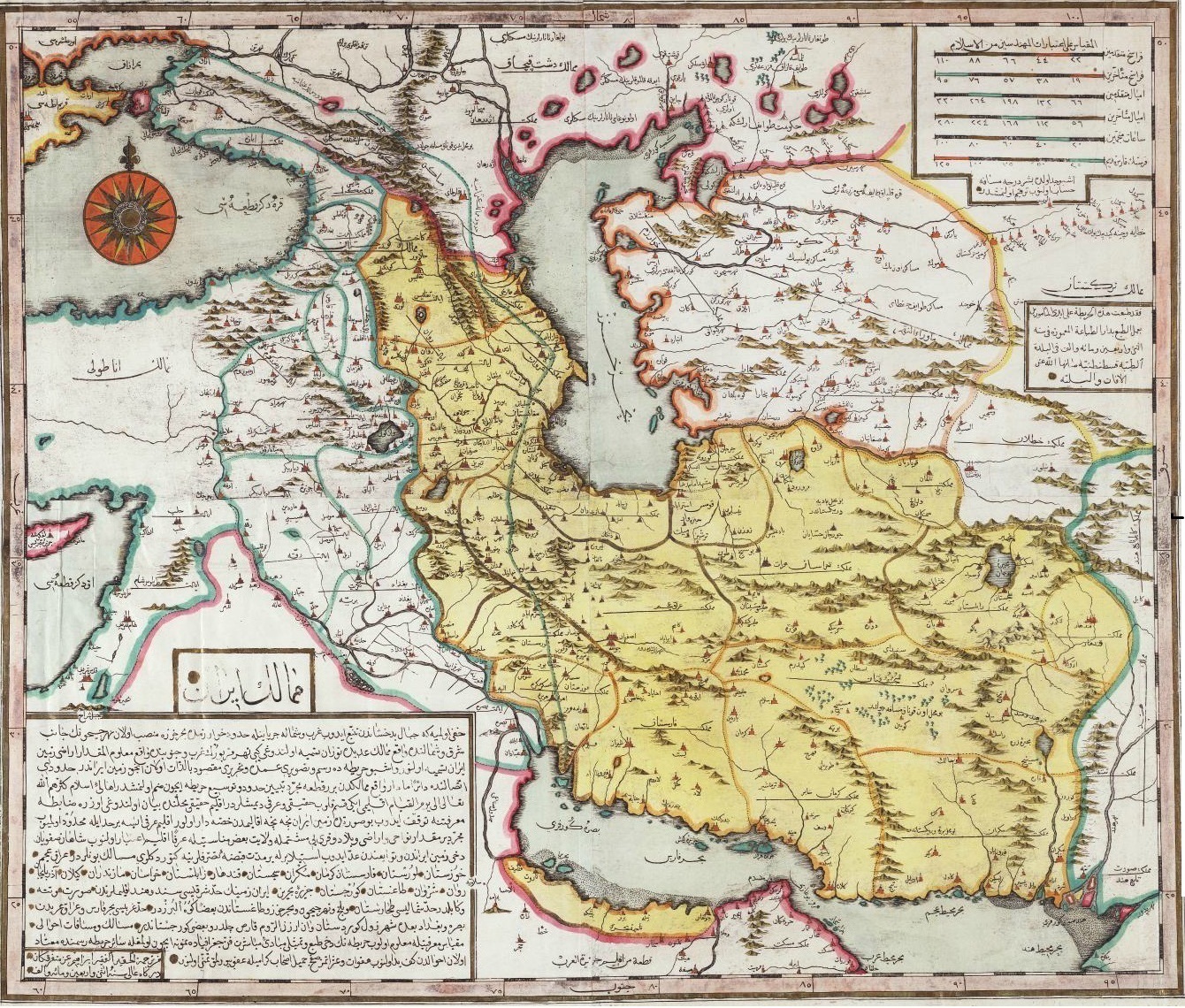
The book has 6 chapters and some document and maps
Summary of Chapter Three of the book “Documents on the Persian Gulf’s name the eternal heritage of ancient time
What's in a name? For the Persian Gulf, quite a lot
The Persian Gulf and its equivalent in different languages has been in used continuously since 2500 years ago in all languages and all over the world specially in the Arab world so that Befor 1960s not even a single case of calling “the Gulf " as the Arabian gulf been found in any text or map specially in Arabic language.
for the first time the new fake name was appeared in Arabic language in 1960s pan Arabism era.Not only ancient and past centuries texts and contracts but also all international organization and institutions also uses and recognize the term Persian Gulf as the valid and accurate term.
Below are Some Historical, Geographical and Legal reason for Validity of the Nomenclature: Persian Gulf .
1- official and unofficial maps and documents in Arabic and other languages
2- official and unofficial agreements and treaties.
3-UN and international organization and international law.
4- historical, religious and geographical books
5- Arab scholars confess for Validity of the Nomenclature:
Persian Gulf .
The necessity for the integrity and unity in writing geographical names and prevention of any ambiguity or multiplicity forced the UN to establish a legal foundation. In 1967, the first conference on the standardization of geographical names was held in Geneva with the participation of scientific and administrative commissions. In the same conference (Geneva), all the Arab countries strongly disagreed with the Israel’s suggestion for changing the name “Gulf of Aqaba”, calling it an improper action. Other countries supported the Arab nations’ concept and finally Israel withdrew its request [3]. From a legal perspective, this action by the Arab countries can be used against themselves in a similar case. “Since 1971 when the incomplete phrase “the Gulf” was first used by a UN letter, protest notes were sent to the UN and it issued a correction and announcing the UN official's rule.
2.1. Naming Background of the Persian Gulf
“The Red Sea was introduced as the Arabian Gulf by Herodotos. In the world map Hecataeus (472 to 509 B.C), the Persian Gulf and Arabian Gulf (Red Sea) have been clearly shown. Also, in the world map of Diseark (285-347 B.C), the Persian Gulf and Arabian gulf are completely distinct”. The ancient Greeks called Pars Sea as “Persian Gulf” and Red Sea as “Arabian Gulf” [4].
***2-2 Persian Gulf in Arabs Contracts and Accords
According to the book “Documents on the Persian Gulf's name”by Dr.Ajam As of 1800 to 1970, at least in 45 contracts concluded among the tribal leader(Emirates) or countries such as Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Ottoman, Oman, Emirs of Motesalehe ( now United Emirates), compiled in English and Arabic, the name of Persian Gulf(khaleej fars) has been used.
:From among the aforesaid contracts the following can be mentioned*
- General contract with Arabian Emirs on Jan. 8, 1820 between Sheikhs of United Emirates atPersian Gulf, signed by General Cair and 11 chiefs of Arab Tribes, the word: Al khaleej Al Farsi(persian gulf) has been used 3 times in the Arabic texts.
- Treaty of 1856 and ۱۹۴۷ on Prohibition of Slaves trades.-
- Permanent Contract of Peace in 1853.-
- Contract on Independence of Kuwait (this deed was registered on June 19, 1961 with Secretariat of United Nations.
- Treaty on Determination of Border Lines ofIraqandKuwait(1996)-
- Even Nasser the pan Arabic leader of Egypt had used the term of (al khaleej al Farsi) Persian gulf in all his speeches and his books and articles before the war of 1967.
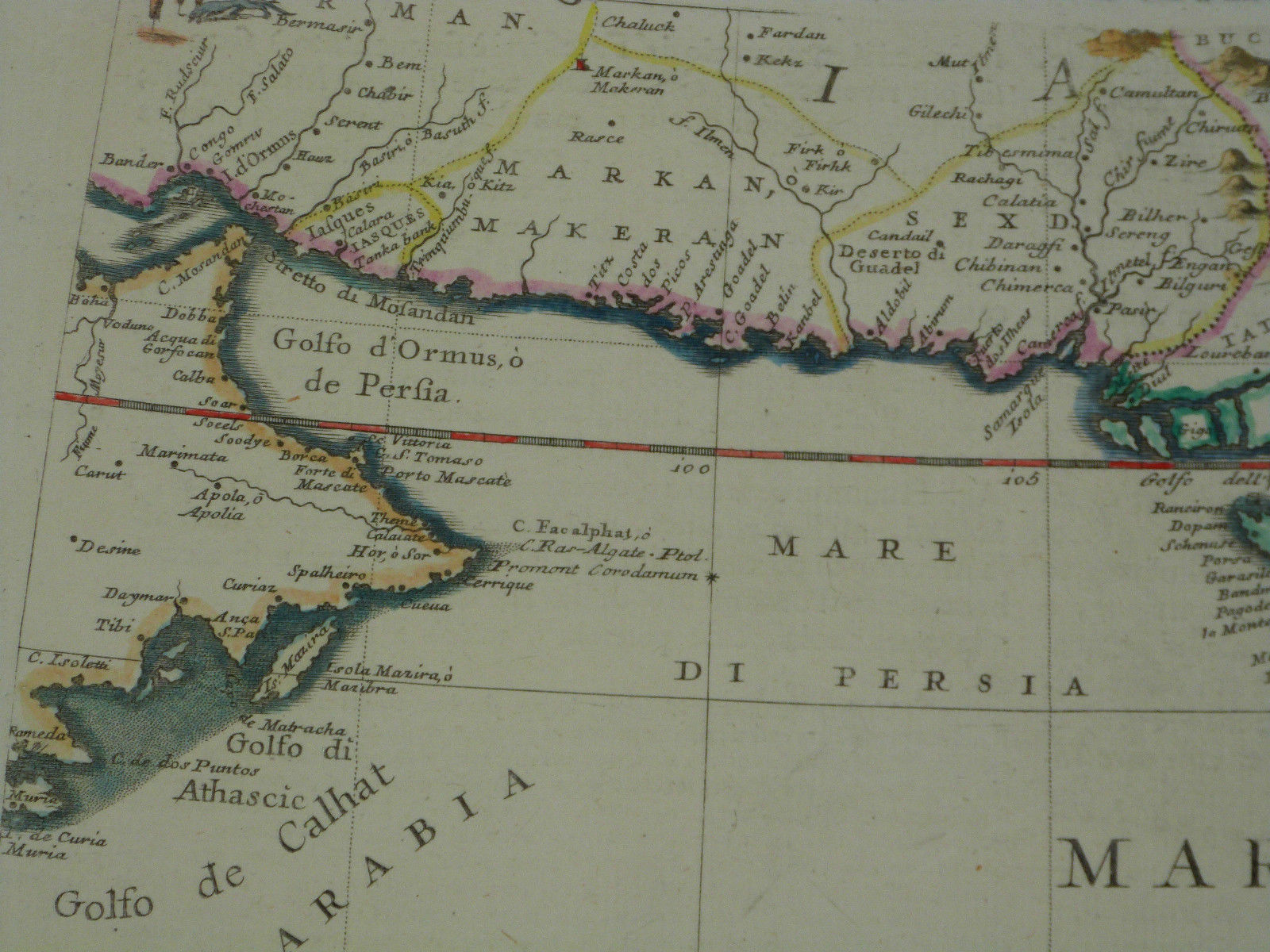
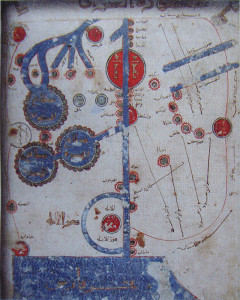
*2- 3 LIST OF SOME EARLY MAPS WHICH HAD MENTIONED THE PERIAN GULF
*****
The earliest known world maps date to classical antiquity, the oldest examples of the 6th to 5th centuries BCE still based on the flat Earth paradigm. World maps assuming a spherical Earth first appear in the Hellenistic period. The developments of Greek geography during this time, notably by Eratosthenes and Posidonius culminated in the Roman era, with Ptolemy's world map (2nd century CE), which would remain authoritative throughout the Middle Ages.
With the Age of Discovery, during the 15th to 18th centuries, world maps became increasingly accurate; exploration of Antarctica, Australia, and the interior of Africa by western mapmakers was left to the 19th and early 20th century.
In all maps, documents and correspondence until 1960, the name of the Persian Gulf and its equivalents were used for body of water between Iran and Arabia.
According to the book “Documents on the Persian Gulf's name”by Dr.Ajam .
A number of these maps and documents are introduced and published in the following Atlases:
1.Atlas of Maps Of the Persian Gulf , Alqasimi, Sultan bin Mohammad, “The Gulf in Historical Maps” 1478- 1861,Leicester, 1996. 2th edition in 1999.
2. Atlas of geographical maps and historical documents about the Persian Gulf from prehistoric times to the present Published by Sahab Institute of Geography and Cartography in 1971 in Tehran.This atlas consists of eight chapters, and 80 maps. The maps collected in this atlas are the work of great geographers and historians of Iranian, Arab, European, Indian, Roman, Egyptian, central Asia, African and American.
3. " Atlas of "Description of the Persian Gulf in Historical Maps" was published in 2008 by the Iranology Foundation, in Iran which presents 40 maps of the Islamic Middle East cartographer and 120 European
maps of colonial era .
4. The Arabian Peninsula in Old European Maps (253 maps) by Khaled Al Ankary, Institute du Monde Arabe,Paris and Tunisia University,2001 .
5. ATLAS OF OLD& HISTORICAL MAPS THE PERSIAN GULF 300BC 2000AD BY Mohammad Reza Sehab . tehran 2005
583 page 2 volum almost 500 maps.
In all the important historical maps and Atlas whether modern or belonging to previous centuries, the water artery located at south ofIranhas been registered asPersian Gulf. In the Arabian countries too, it has always been namedPersian Gulfup to the 70s. For instance, in the Atlas “Al araq fi Al khavaret Al ghadimeh” by Dr. Ahmad Souseh (Baghdad 1959) including 40 maps among the Arabian sources of the Middle Ages all have the Arabic term for the Persian gulf.
In the maps presented by Arabian countries to the International Court of the justice for settlements of border claims, the name ofPERSIAN GULFhas been mentioned in their documents.
– Atlas of La Péninsule Arabique dans les cartes Européennes Anciennes (The Arabian Peninsula in Old European Maps).Paris, Monde Arabs institute and Tunisia university IMA & Khaled. Al Ankary, 2001. ۴۲۴ pp. contains ۲۶۰ maps with details about each map in 3 languages: Arabic, English and French. Almost all of these 260 maps have the correct name of Persian Gulf.
Moreover, 10 maps have used both Persian Gulf for the gulf and also persian Sea (for the current area of Seaof Oman and Arabian sea) •
The book: Roots of Kuwait. “Osoul Alkuwait Almanshour Alalam” (1991) published in theNetherlandsalso contains 15 maps where the name of PERSIAN GULFexists.
- In the “Atlas of Alkuwaitfi Al kharaet Al Aalam” some maps have been used where there exists the name ofPERSIAN GULF.
In Atlas of “Alkuwaitfi Al kharaet Al tarikhieh” published by the efforts of Abdollah Yousef Al ghanim in 1994, there are about 200 maps mentioning the name ofPersian Gulf
- In the ARABIC book: “Al khaleej al fars Aber Al tarikh va Al ghoroun” (written by Mohammad Mirza, 1976Cairo) there are 52 maps drawn out of Arabic sources, all have the name ofPersian Gulf.
- In Atlas of “History of Islam” (1951-55AmericaandEgypt) the namePersian Gulf has been mentioned IN ۱۶ MAPS.
- In the Atlas of “Khalij (Gulf) in the Historical Maps” published in UAE (۱۹۹۹) more than 600 maps have the term Persian gulf.
- The Arabic Bank and Beyt Al quran inBahrainpublished a large wall calendar in 1996 containing the 11 historical map ofBahrainin which all the maps contain the name ofPersian Gulf
It is interesting that from among 6000 existing historical maps published up to 1890, there are only three maps mentioning the names of Basreh Gulf, Ghatif Gulf, and Arabic Gulf, this name in fact are the name of bays of the Persian gulf. in local language they call the bay also as the gulf like :gulf of Busher-ChahBahar Gulf,SirafGulf,BasrehGulf,Ghatif Gulf,Bahrain Gulf, Basre gulf …. but such names are not applied to the entirety of the Persian Gulf.
It is obvious that the promotional use by the Arabs of the three aforementioned maps, whose identity and originality are not clear, in comparison with 6000 maps and more than 300 historical and credible geographical books from ancient time to 20thcentury , shall lack any value.
In the Arabic Dictionaries like Al Monjed, and also in all (60)Qoranic Tafsires and religious Islamic books and in all treaties ( more than 30 Arabic treaties between the Arabs tribe leader with theUKand Othman and Iranians )Persian gulfhas been used .
In the many museums all over the world some can find maps or manuscript having the name Persian gulf some recorded as intangible world heritage (UNESCO) In Library of American Congress, Britain National Library (London), deeds at Ministry of India’s Affairs (London), Library of Faculty of Orientals Studies of London, there are more than 300 maps, containing the name Persian Gulf. In Eskandria Library of Egypt And National Musum Of Egypt alsoPersian gulfmap are preserved.
Furthermore, about 30 valid Atlas have registered the name ofPERSIAN GULFwithin the past 300 years, such as: Atlas of Thomas Herbert (1628).
– Atlas of Pars,LousajUniversity(1863). – Atlas ofGermany(1861), Pars Envile Atlas (1760).- Atlas of Modern Geography (1890).- Atlas of London (1873),- Atlas of Ernest Embrosius (1922),- Atlas of Bilefild (1899)- Atlas of Harmsorth (19th Century, London). – ….
In 18th to 20th centuries when the UK expanded its dominance over the seas and appeared as protectorate of the Sheikhs on the south sectors of the PERSIAN GULF, the official maps and documents of the areas in all languages refers to the GULF as PERSIAN GULF.
Applications of the Name Persian Gulf by International Organizations
Not only the Persian Gulf had been used since ancient time in all languages but also in current time non Arabs countries had never recognized a new tribal name and UN and all international Organizations and affiliated foundations have applied the correct name of PERSIAN GULF.
In the Arabic text of the UN some time had appeared wrong term but as soon AS the secretariat have considered it the correction have been done.
For the first time in 1971 in a UN text wrong term was used and then was corrected by a UN instruction and Note No. AD311/1GEN dated March 5, 1971.
Differentiation between Persian sea and Persian gulf
The Arabian Sea historically and geographically has been referred to with different names by Turks, Persian and Arabs,expert of Geography and cartography in medieval Islam, usually named Persian sea a sea from east vak vak island (including Thailand coast and Andaman sea to the west Basra bay ) some of them called all body of water in north Indian ocean as the Persian sea (Bahre Fars) and separate it from Persian gulf (AlKhaleej AlFars ) some European geographers and travelers, also Differentiated between Persian sea and Persian gulf *** Persian SeaIbn al-Wardi and some of the geographers of Geography and cartography in medieval Islam were using the word Bahre Fars بحر فارس (Persian sea) to mention the current body of water in the north of Indian Ocean , Ibn Khordadbeh, Ibn Sa'id al-Maghribi, Muhammad al-Idrisi, Istakhri, Mahmud al-Kashgari, Khashkhash Ibn Saeed Ibn Aswad and Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi had mentioned the sea as Persian sea and sea of Mokran. some of the medieval map including the map by Vincenzo Maria Coronelli, 1693 had mentioned the Persian sea and also Makran. Cornelius Le Brun's Year 1718 Map.in the 16th century map by Abraham Ortelius in which the name of the Persian Sea and the Indian Sea appear.. Zakariya al-Qazwini, Al-Masudi , Ibn Hawqal, , (Hafiz-i Abru),mentioned in the book History of Islam and Iran, says:"the Green Sea is also called the Sea of India and it connects with the Persian Sea.” . Arabian Sea was first used on European maps in the colonial period . Ibn Khordadbeh, Ibn al-Faqih, Ibn Rustah, Sohrab, Ramhormozi,. Abu Ishaq Ibrahim ibn Muhammad al-Farisi al Istakhri, Abu al-Hasan Ali ibn al-Husayn ibn Ali al-Mas'udi, Al-Mutahhar ibn Tahir al-Maqdisi (d. 966), Ibn Hawqal, Al-Muqaddasi, Ibn Khaldun, Mohammad ibn Najub Bekiran, Abu Rayhan Biruni, Muhammad al-Idrisi, Yaqut al-Hamawi, Zakariya al-Qazwini, Abu'l-Fida, Al-Dimashqi, Hamdollah Mostowfi, Al-Nuwayri, Ibn Batutta,Katip Çelebi and other sources have used the terms, "Bahr-i Mohit i Ajam", "Bahr-al-'Ajami", "Bahr-i-Fars", "Dera-i-Fars"(Persian), and "Bahr-i Mokran/Mecran", "Bahr-i Al Akhzar" (green) to refer to the current Arabian sea. ("Bahr-in Arabic means Sea" and Mohit means ocean) none of them had referred to as Arabian Sea.
- In the Book Documents on the Persian Gulf's name( https://kids.kiddle.co/Documents_on_the_Persian_Gulf%27s_name)
Pages 60 to 84 are devoted to the description of the Persian Sea in the books of geographers and historians of Muslim world
All of whom had called the seas of south part of Iran , india and the Arabian Peninsula as the Persian Sea, the book cited description of the Persian sea from the book (Sourat Ard)Face of the Earth page 42 Written by Ibn Hawql: ” … after Arabs lands then should be mentioned The Sea of Persia because Persian sea includes most of Arabs borders, and the Arab peninsula are connected to this sea ,the Persian sea connected to many countries of Islam. this sea start from the Qulzam(Red sea ) it ends to Eble (Basra bay), then It crosses Siraf (Bushehr) then extends to the coasts of Hormuz then Makran and the coasts of Multan, which is the coasts of Sindh (Pakistan) which the boundary of the country of Islam has ended then the persian sea continues to the coasts of India then connect to to the sea of China”. see original text: https://al-maktaba.org/book/11780/47
Persian Sea, the old name of the vast sea covering all southern seas of Iran and many other part of the west Asia . Muslim geographers referred to a wide body of water as the Persian sea,they were considering the excist of only have 7 seas in the world and the blived the vast sea was th persian sea and Rum sea.
· some other scholar of medieval Islam who mentioned persian sea are :
In 290 (Islamic calender.H ) Ibn Rasta, separated the Persian Gulf from vast sea of Persian sea for the first time, (book Al-A'laq al-Nafisa, p. 84);
in 266 (Islamic calender.H ), Qadama Ibn Ja'far called it the Persian Sea (p. 233).
in 290 I.C.H , Sohrab (Ibn Sarabiun) called it the Persian Sea and the sea of the Persia (pp. 59,78);
in 332 (Islamic calender.H ) Masoudi (edition 1967, p. 38, vol. 1, p. 128) has explained it as the Persian Gulf branch of the Persian Sea.
In 340 Istakhri (1967, p. 28), and in 342 Bozorg Ibn Shahriyar Ramhormozi (p. 41) and in 375 Mohammad Ibn Ahmad Moghaddasi (pp. 17-18) called it the Persian Sea and in 355 Motahar Ibn Tahir Moghaddasi (vol. 4, p. 58) said the Persian Gulf a branch of the Persian sea
in 367 Ibn Hawql (p. 42) the Persian Gulf and the Persian sea
in 372 Sahib Hudood al-Alam (p. 12) it is the Persian sea
in 420 Abu Rihan al-Biruni (p. 167) the Persian Sea and the Persian Gulf.
In the book Masalak al-Mamalak, the Persian translation of the fifth / sixth century AH the Persian Sea is the great sea, (Istakhri, 1989, p. 109).
In 500 AH the book of Ibn Balkhi it described the Persian Sea (p. 153)
in 605 Muhammad ibn Najib Bakran called it the Persian sea (p. 18,20)
· in 625 the Yagout described the Persian Sea (vol. 1, p. 502),
· in the eighth century Hamdollah Mostofi Persian sea from Sindh to Oman has been recorded as part of the Persian Sea (p. 136).
In the third century, Ibn Faqih connected the Persian Sea to the Indian Sea and considered both as one sea (p. 8).
According to Ibn Rasta, the Persian Gulf branched off from the Indian Sea (p. 84).
Istakhri considered the extent of the Persian Gulf as far as India (edition 1967, pp. 28-29) and in the book Hudood al-Alam as its limit up to the Indus (p. 12).
· According to Ibn Balkhi, the Persian Sea was connected to the Red Sea (ibid.)
Idrisi wrote the green sea is the Persian Sea and blived it is connected to the China Sea (Vol. 1, p. 9). Yaghoot also considers the Persian Gulf as a branch of the Great Indian Sea . http://lib.eshia.ir/23019/1/577 This shows that befor and in colonial times, the Arabian sea was not used by arabs and muslems scholars .
^"The Voyage around the Erythraean Sea". depts.washington.edu.- ^"Archived copy". ^Mitchell 1831.
- ^“A Jewel of Ottoman Naval History: The Book of Kâtip Çelebi on Naval Campaigns" in the MuslimHeritage.com
- ^"Ottoman Maritime Arsenals And Shipbuilding Technology In The 16th And 17th Centuries" Archived 2013-10-14 at the Wayback Machine in the MuslimHeritage.com
- ^http://www.persiangulfstudies.com/fa/pages/875/دریای-مکران-یا دریای عرب
- ^"persian sea bahre fars: Author: group of Writers". http://wikifeqh.ir.
- ^"Al-Massalek wa al-Mamalek", Leiden edition, 1889. p. 233
- ^The abrdiged "Al-Buldan", Leiden, 1885, p. 8
- ^Ibn Rustah, Kitāb al-A'lāk an-Nafīsa, ed. M. J. De Goeje, Bibliotheca Geographorum Arabicorum [BGA], Leiden, E. J. Brill, 1891/1892. p. 81
- ^Ajayeb al-Aqalim al-Saba ila Nehayate al-Mara, (Vienne: 1929), p. 59. 9th century AD.
- ^Nakhoda Bozorg ibn Shahriyar Ramhormozi was another Persian geographer of the classical Islamic era, "Ajayeb al-Hind", ed: M. Davis, Leiden 1886, p. 41
- ^"Massalek al-Mamalek", ed.: De M.J. Goeje, Leiden 1927, p. 28
- ^"Muruj adh-dhahab wa ma'adin al-jawhar (The Meadows of Gold and Mines of Gems)", English Translation by Aloys Sprenger, Vol I, (London: 1841), p. 259
- ^al-Bad’ wa-l Tarikh, (Paris: 1907) Tom IV, p. 58.
- ^"The Oriental Geography of Ebn Hawkal", Translated by Sir Williams Ouseley (London: 1800) p. 62; "Surat al-Arḍ"(Leiden 1938), Vol I, p. 42.
- ^Ahsan al-Taqasim fi Ma’rifat al-Aqalim. Ed: De A.J. Goeje, (Leiden 1906), p. 17.
- ^"Jahan Nama", Vol I. p. 44. .
- ^"Al-Tafhim le-awa’el Sena al-Tanjim" ed.: Jalal al-Din Homai (Tehran: 1318 Hijri Sola Calendar), p. 167. Also in "Qanun Masudi"(Heydarabad, 1955), Vol. II. p. 558.
- ^"Geographic d’Edirisi" traduite de l’Arabe en Francais par P. Amedee Jaulert (Recueil des voyages et des memoires publiees par la Societe de Geographie), (Paris: 1840), Vols. VI and VI. "Nuzhat al-Mushtaq fi Ikhtraq al-Afar", (Rome : 1878). p. 9
- ^"mu’jam al-Buldan",(Cairo: 1906), Vol. 2, p. 68.
- ^"Athar al-Bilad" (Gutingen: 1848), p. 104.
- ^"Taqwim al-Buldan", Geographie d’Aboulfeda traduite de l’Arab par M. Reinaud, 2 Vols. (Paris: 1848), Vol 1, p. 23.
- ^ Jump up to:abQuoted also in Mohammad Javad Mashkoor in an article titled "Nam-i Khalij Fars" in the proceeding of the "Seminar on Khalij-e-Fars" (Tehran: 1964). p. 46.
- ^"Nuzhat al-Qolub", ed: Mohammad Dabir Sayaqi, (Tehran: 1336 Hijri Solar Year), p. 164.
- ^"The Travels of Ibn Babutta", translated from the abrdiged Arabic MMS of Cambridge by the Rev. Samuel Lee(Cambridgde: 1824), p. 56
- ^http://www.persiangulfstudies.com/fa/pages/875/دریای-مکران-یادریای عرب
https://www.sid.ir/fa/journal/SearchPaperlight.aspx?str=%D8%A8%D8%AD%D8%B1%20%D9%81%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%B3
«بحر فارس» و «خلیج فارس» فی المعاجم اللغویة والمصادر الأدبیة
عجائب بحر الهند و فارس و جزائره
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SZiEILb_Rxk
https://sonsofsunnah.com/2015/09/11
bahre Fars in holy books
https://www.gisoom.com/book/11138166/%DA%A9%D8%AA%D8%A7%D8%A8-%D8%A8%D8%AD%D8%B1-%D9%81%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%B3-%D9%88-%D8%AE%D9%84%DB%8C%D8%AC-%D9%81%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%B3-%D9%81%DB%8C-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85%D8%B5%D8%A7%D8%AF%D8%B1-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B9%D8%B1%D8%A8%DB%8C%D9%87-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%82%D8%AF%DB%8C%D9%85%D9%87/
https://www.adinehbook.com/gp/product/6007544001
http://wikifeqh.ir/%D8%A8%D8%AD%D8%B1_%D9%81%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%B3
http://ensani.ir/fa/article/195419/-%D8%A8%D8%AD%D8%B1-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%81%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%B3%DB%8C-%DB%8C%D8%A7-%D8%A8%D8%AD%D8%B1-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B9%D8%B1%D8%A8-%D8%A8%D8%A7-%D9%87%D9%85-%D8%AA%D8%AD%D8%B1%DB%8C%D9%81-%D8%AA%D8%A7%D8%B1%DB%8C%D8%AE
https://wikinoor.ir/%D8%B9%D8%AC%D8%A7%D8%A6%D8%A8_%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%87%D9%86%D8%AF_%D8%A8%D8%B1%D9%87_%D9%88_%D8%A8%D8%AD%D8%B1%D9%87
https://www.noorlib.ir/view/fa/book/bookview/text/23584/1/328
کتاب عجائب الهند : بره وبحره وجزایره / تألیف بزرک بن شهریار الناخداه الرامهرمزى.
مصر : مطبعة السعاده،
تاریخ الإصدار 1908
https://www.noorlib.ir/View/fa/BookAlphabet?SearchText=%D8%AA%D9%82%D9%88%D9%8A%D9%85%20%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A8%D9%84%D8%AF%D8%A7%D9%86
بحر فارس تقویم البلدان
https://www.noorlib.ir/View/fa/Book/BookView/Image/6172/1/25?SearchText=%D8%A8%D8%AD%D8%B1%20%D9%81%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%B3&Sort=score-desc&PageNo=1&PageSize=10000&Origin=noorlib.web.app
Clearly separated Persian sea and Persian gulf as 2 different body of water
Many atlases had published old maps of Asia and Indian ocean such as Atlas of La Péninsule Arabique dans les cartes Européennes Anciennes (The Arabian Peninsula in Old European Maps).Paris, 424pp. contains 260 maps Almost all of these 260 maps have the name of Persian Gulf. Moreover, 10 maps have used both Persian Gulf for the persian gulf and also persian Sea (for the body of water which is now called Arabian sea)- * Some of the most important historical atlases of the persian gulf are as:
- ۱- Atlas of The Arabian Peninsula in Old European Maps (253 maps) by Khaled Al Ankary, Institute du Monde Arabe,ParisandTunisiaUniversity,2001
all 253 maps of this atlas has been printed in color and 3 languages and have the corect name of Persian gulf also the maps in pages:-141-226-323-322-331-345-347-363-355 have mentioned persian gulf for the Gulf and also persian sea for the body of water of current Arabian sea and Oman gulf , such as the hours shape map of Bunting H.S.Q34/24CM Hanover,1620.
۲- Atlas of Historical maps of the gulf by sultan muhammad al qasimi Sharjeh 500 maps of the persian gulf .
- ۳- Atlas of Iraq in old maps. by Ahmad Sussa 39 old maps of Arabic and Islamic sources all have the correct name of persian gulf(Bahre Fars)
- ۴- Atlas Kuwait in the maps of the world 1992 . contain 80 maps all have the Persian gulf name.
- ۵- Atlas Kuwait reading the historical maps, 200 maps ,1994 .
- ۶- Atlas of Roots of Kuwait, 15 maps ,1991.
- ۷- description of the Persian gulf in the historical maps by Iranology foundation, 40 maps of Islamic scholars and 120 maps of European famous cartographers 0f 1500-1900 AD.by Dr Hassan Habibi 2007.Tehran.

.all the maps have the name Persian gulf. and many other atlases have also been published and they have been described in the book: Documents on the Persian Gulf’s name
List of some early maps which had mentioned the Persian Gulf and also some famous atlases explained the Persian Gulf:
- Map of Babylonianmaps. Babylonian Map of the World. the oldest known world map, 6th century BCE Now in the British Museum.
- Map of Anaximander world map-Reconstruction of Anaximander's map
- Map of Hecataeus world map- Reconstruction of Hecataeus' map
- Map of Mappa di Eratostene.1883 reconstruction of Eratosthenes
- Map of World map hedo.A 1628 reconstruction of Posidonius ideas about the positions of continents (many details couldn't have been known by Posidonius)
- Map of Map Pomponius Mela rotated.An 1898 reconstruction of Pomponius Mela's view of the World.
- Map of Ptolemy-World Vat Urb 82.The oldest surviving Ptolemy's world map Ptolemaic world map, redrawn according to his 1st projection
- by Orthodox monasticismmonks at Constantinople under Maximus Planudes around 1300
- Map of Ptolemy World Map.Nicolaus Germanus's 1467 Latin world map according to Ptolemy's 2nd projection, the first known to the west
- Map of World Map by Cosmas Indicopleustes.
- Map of Ibn Howqal World map. by Ibn Hawqal (south at top)
- Map of Cotton world map.The Anglo-Saxon 'Cotton' world map (c. 1040).
- Map of Beatus map.World map from the Saint-Sever Beatus
- Map of Kashgari , Mahmud al-Kashgarial-Kashgari's ''Diwanu Lughat at-Turk''.
- Map of Tabula Rogeriana upside-down. (1154).
- Map of Hereford Mappa Mundi 1300.The Hereford Mappa Mundi.
- World map pietro vesconte. Pietro Vesconte's world map, 1321
- Map of Catalan-Atlas - Two leaves of The world atlas
- Map of Da-ming-hun-yi-tu.Da Ming Hunyi Tu map
- Map of KangnidoMap.Kangnido world map (1402)
- Map of DeVirgaDetail.De Virga world map (1411–1415)
- Map of Biancomap.Bianco world map (1436)
- Map of Mapa_de_Borgia_XV.Borgia map (early 15th century)
- Map of Genoese map.Genoese map of 1457, Biblioteca Nazionale at Florence
- Map of FraMauroDetailedMapInverted.Fra Mauro map (1459)
- Map of Martellus world map.Martellus world map (1490)
- Map of Behaims Erdapfel.Behaim's Erdapfel
- Map of Juan de la Cosa-North up.Map of Juan de la Cosa, shown rotated right (in the original manuscript north points left), 1500
- Map of Cantino planisphere 1502, Biblioteca Estense, Modena
- Map of Caverio Map circa 1506, Bibliothèque Nationale de France, Paris
- Map of Ruysch map.Johannes RuyschRuysch's 1507 map of the world
- Map of Waldseemuller map 2.Waldseemüller map with joint sheets, 1507
- Map of Piri reis world map 01.Fragment of the Piri Reis map by Piri Reis in 1513
- Map of Piri reis world map 01.Piri reis world map 01
- Map of PietroCoppo.Map of Pietro Coppo, Venice, 1520
- Map of Map Diego Ribero 1529.World Map by Diogo Ribeiro, "Propaganda map" (1529), Biblioteca Apostolica Vaticana
- Map of Mercator 1569.pngGerardus MercatorMercator ''Nova et Aucta Orbis Terrae Descriptio'', 1569.
- Map of Abraham OrteliusOrtelius' world ''Theatrum Orbis Terrarum'' (1570)
- Map of 1581 Bunting clover leaf map.''Die ganze Welt in einem Kleberblat'' (The entire World in a Cloverleaf). Jerusalem is in the centre
- of the map surrounded by the three continents.
- Map of Kunyu Wanguo Quantu (坤輿萬國全圖). (1602), Japanese copy
- Map of Nova totius Terrarum Orbis geographica ac hydrographica tabula (Hendrik Hondius) balanced. IIHendrik Hondius,
- ''Nova Totius Terrarum Orbis Geographica ac Hydrographica Tabula'', 1630
- Map of Orbis Terrarum Nova et Accuratissima Tabula by Nicolaes Visscher, 1658.
- Map of 1794 Samuel Dunn Wall Map of the World in Hemispheres - Geographicus World2-dunn-1794. (mathematician)
- World Map 1689. Van Schagen's map of the world, 1689
- Map of persia. Persian Gulf 1747 Boen.
- Persian(IRAN) Empire 1747. karta Persian Gulf1747
- Saudi King letter.Saudi King letter PERSIAN GULF
- ALKHALEEJ ALFARSI 1952.Saudi map of Persian Gulf
- Map of Iraq in Iraqi carpet 1970. Persian Gulf Iraqi carpet 1970.
- Basra bahrefars.turkey: BahreFars( Persian Gulf)
- Cairo street..A street in Cairo named Persian Gulf 1958
- Heinrich Kiepert. Imperia Persarum et Macedonum. 1903. Persian Gulf.
- Soulier, E.; Andriveau-Goujon, J. Anciens Empires Jusqua Alexandre. 1838.
- Map Pomponius Mela rotated.An 43 AD.Karata Persian Gulf
- Ptolemy Cosmographia 1467 - Arabian peninsula. Persian Gulf .
- Mappa di Eratostene. 194 BC Eratosthenes karta Persian Gulf
- Istakhri map 2.Regional - Persian Gulf Istakhri,1200
- Ottoman Asia (partial, 1893).1893 Karata Persian Gulf (Ajam)
- Saudi map of Persian Gulf 1952. الخلیج الفارسی.
- Map of Persial Gulf- Amsterdam-1640.Karata Persian Gulf 1640
- Map of the region bounded by the Saudi Peninsula, Red Sea. Jacob van Merus, 1680,Karata Persian Gulf Amesterdam
- Regno di Persia con le notitie delle ... Publication Date 1679 Scarce map extending from the Eufrate to the Indo.Showing major rivers, mountains and cities. From Il Mercurio, by De Rossi. 1679 .
- Perse Turquie Asiatique et Arabie old map Desnos 1766. Persian Gulf
- Antique map La Perse Bellin 1764.Karata Persian Gulf 1764'''
- Persia Sive Sophorum regnum Old map Persia Merian 1638.
- Jansson's map of Persia..Amsterdam karta Persian Gulf1640
- Map of Asia in the shape of the mythical winged horse Pegasus.. 1581 Hannover Karata Persian Gulf
- 1732 Asia issued.. 1732 Guillaume Danet. Persian Gulf
- Map of Amsterdam1685.. Karata Persian Gulf 1700
- Detailed map of Asia..Nuremberg / 1744 karta Persian Gulf
- Important Jodocus Hondius.... Amsterdam 1620 karta Persian Gulf
- Published in Amsterdam.png by Nicholas Visscher the Elder.1670.
- Map of K. Johnston -1850-Edinburg.A.K. Johnston -1850-Edinburg
- Map of George Rollos 1770 London.
- Map of Guillaume de L'Isle - 1731- Paris.
- Map of J. Rapkin , Published by Tallis.-1851-london.1851-
- Location of and gulf by Janssonius, Joannes- 1640-Amsterdam.
- Map of Mercator, Belgium, 1578.Mercator, Belgium, 1578
- Map of Published by D'Apres de Mannevillette-1775-paris .
- Map of Robert- 1760- Paris. 1760- Paris .
- Map of The London Geographical Institute 1890, Published by George Philip & Son. 1890, Persian Gulf
- Map of V. Levasseur - Paris- 1838.V. Levasseur -
- Amsterdam J. Covens et C. Mortier,1720.Amsterdam 1720 Persian Gulf
- Strassbourg 1525 by Lorenz (Laurent) Fries.Strasbourg 1525 karta Persian Gulf
- Rigobert Bonne- 1771 Paris.Rigobert Bonne- 1771 Paris.
- Map of Nova Orbis Tabula In Lucem Edita, A.F.de Wit.. Amsterdam-1680 ca Karata Persian Gulf
- Map of Typus Orbis A Ptol. Descriptus.-1542
- Map of Die beyden Halbkugeln.'''Die beyden Halbkugeln-Vienna-1790'''
- Mappemonde a l'usage du Roy Par Guillaume Delisle Premier. 1720 (Shows De Gama Land)
- Mappe Monde Carte Universelle de la Terre Dressee Sur les Relations les plus nouvelles.Karata Persian Gulf -1755'''
- Persia, Caspian Sea, done by ye Czar, and Part of Independent Tartary. 2700 Persian Gulf
- Middle East Antique map Babylon Assyriens Philippe 1787. Persian Gulf
- Map of Persia Kingdom Ormus Strait Hormuz Old plan Bellin 1756.
- Japanese Map of Saudi Arabia.Japanese karta Persian Gulf1874
- Brodersen, Kai. 2012. "Cartography." In ''Geography in Classical Antiquity.'' By Daniela Dueck, 99–110. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ. Press.
- Edson, Evelyn. 1993. "The Oldest World Maps: Classical Sources of Three Eighth Century Mappaemundi." ''Ancient World'' 24.2: 169-184.
- Fox, Michael, and Stephen R Reimer. 2008. ''Mappae Mundi: Representing the World and Its Inhabitants In Texts, Maps,
- and Images In Medieval and Early Modern Europe.'' Edmonton, Alberta: Department of English and Film Studies, University of Alberta.
- Goffart, Walter. 2003. ''Historical Atlases: The First Three Hundred Years,
1570–1870.'' Chicago: Univ. of Chicago Press.
- Harwood, Jeremy, and A. Sarah Bendall. 2006. ''To the Ends of the Earth: 100 Maps That Changed the World.'' Cincinnati, OH: David & Charles.
- Harvey, Paul D. A., ed. 2006. ''The Hereford World Map: Medieval World Maps and their Context.'' London: British Library.
- Shirley, Rodney W. 1983. ''The Mapping of the World: Early Printed World Maps 1472-1700.'' London: Holland Press.
- Talbert, Richard J. A., ed. 2000. ''Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World.'' Princeton, NJ: Princeton Univ. Press.
- Wendt, Henry, John Delaney, and Alex Bowles. 2010. ''Envisioning the World: The First Printed Maps 1472–1700.'' Santa Rosa, CA: Sonoma County Museum.
- Woodward, David. 1985. "Reality, Symbolism, Time, and Space in Medieval World Maps." ''Annals of the Association of American Geographers'' 75.4: 510-21.
- The Arabian Peninsula in Old European Maps (253 maps) by Khaled Al Ankary, Institute du Monde Arabe,Paris and Tunisia University,2001 .
- Tibbets,Gerald Randall,Arabian in early Maps,Naples,Italy,Falcon press, 1978.
- A Guide to Antique Maps Collection of king Abdulaziz Public Library,Riyadh.
- Atlas of the Arab World and the Middle East ; With an Introduction [entitled The Arab World] by C.F. Beckingham ,Macmillan, 1960
- Theatrum Orbis Terrarum (Ortelius, Netherlands, 1570–1612)
- Piri Reis Map (Ottoman Empire, 1570–1612)
- Mercator's Atlas (1578)
- Atlas Novus (Blaeu, Netherlands, 1635–1658; 1645 edition at UCLA)
- Dell'Arcano del Mare (England/Italy, 1645–1661)
- Cartes générales de toutes les parties du monde (France, 1658–1676)
- Klencke Atlas (1660; world's largest book)
- Atlas Maior (Blaeu, Netherlands, 1662–1667)
- Atlante Veneto (Coronelli, Venice, 1691)
- Britannia Depicta (London, 1720)
- Atlas Nouveau (Amsterdam, 1742)
- Cary's New and Correct English Atlas (London, 1787)
- Andrees Allgemeiner Handatlas (Germany, 1881–1939; in the UK as Times Atlas of the World, 1895)
- Atlas do Visconde de Santarem (Paris, 1841, 1842-1844, and 1849)
- Bosatlas (Netherlands 1877–present)
- Cedid Atlas (Istanbul, 1803)o
- Rand McNally Atlas (United States, 1881–present)
- Stielers Handatlas (Germany, 1817–1944)
- Atlante Internazionale del Touring Club Italiano (Italy, 1927–1978)
- Atlas Mira (Russia, 1937–present)
- Geographers' A–Z Street Atlas (United Kingdom, 1938–present)
- Gran Atlas Aguilar (Spain, 1969/1970)
- Historical Atlas of China (Taiwan, 1980)
- The Historical Atlas of China (China, 1982)
- National Geographic Atlas of the World (United States, 1963–present)
- Pergamon World Atlas (1962/1968)
- Times Atlas of the World (United Kingdom, 1895–present)
- Dorling Kindersley Atlas of the World 1994–present
- Digital atlases
- Further information: Geographic information system, List of online map services, Web mapping, and Comparison of web map services
- TerraServer-USA/MSR Maps (1998)
- NASA World Wind (2003)
- Google Maps (2005)
- North American Environmental Atlas (2005)
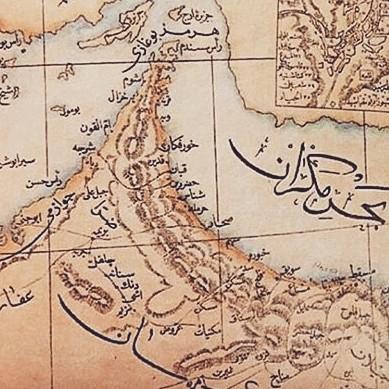
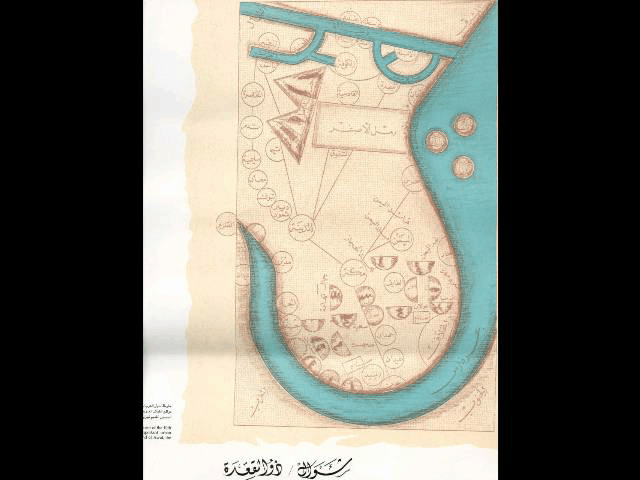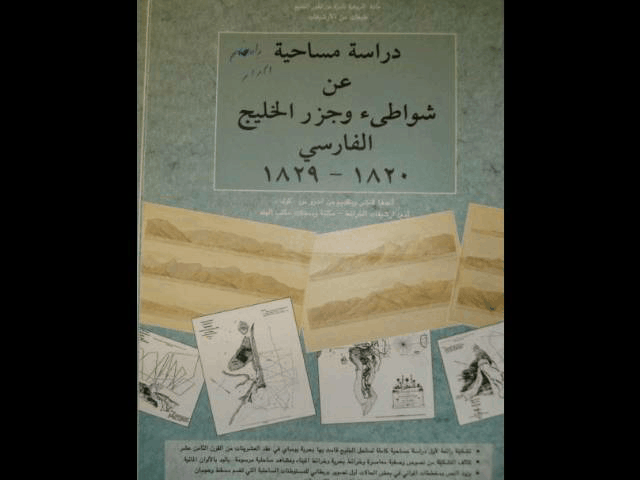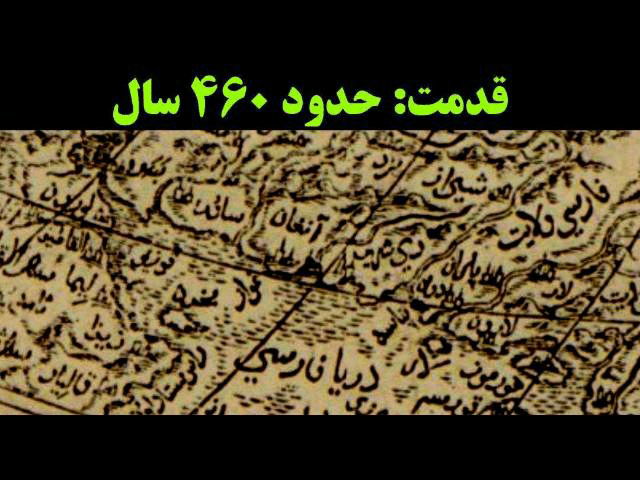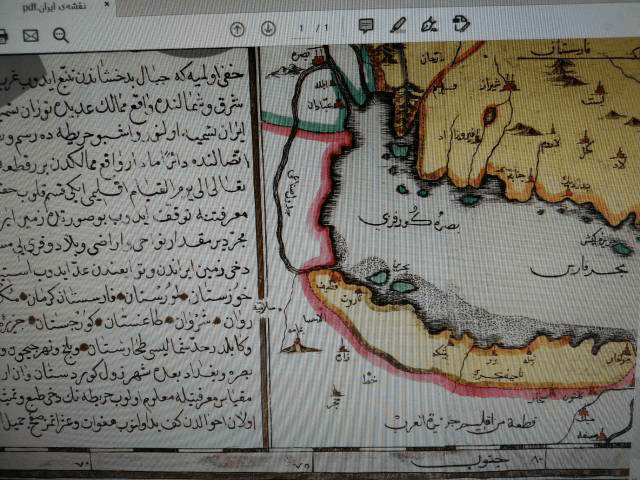
*Some 121 historical maps with reference to the Persian Gulf
from 6th to 20th century.
01-
Map_of_the_World_6th_century_Original_and_reconstOne of the oldest surviving
European maps from Byzantine era with the word 'Sinus Persicus' .C. 6th century CE
02
Reconstruction Avezac of a world map by Anonymous Geographer from Ravenna .C. 700 CE
03
Reconstruction Avezac of a world map by Anonymous Geographer from Ravenna.C. 700 CE
04
Istakhri_map_Bahr_Fars.Regional map showing the word Bahr Fars, (Persian sea)
in Arabic, from the text of Al-aqaalim by the Persian geographer Istakhri.C. 9th century
05
Persian_Gulf_11th_century_Arabic_Manuscript.An Islamic map showing Persian Gulf . 320 A.H. (932 CE)
06
Abu Raihan Biruni world map of the distribution of land and sea,C. 1029
07
Persian_Gulfs_Biruni_Map.Haft-Darya (seven Seas).C. 1029
08
Saint Sever map of the world.after Beatus1030.C.
09
Mappa_di_Eratostene-19th_.C.Reconstruction of 194 BCE Eratosthenes map..C. 19th Century
10
Ptolemy_World_Map_15th_Century.jpg (153015 .)
A map based on Ptolemy's Geography for comparison. The work uses the phrase Persicus Sinus..C. 15th century
11
Ptolemaei_Kartor_early_1400 Dati, La Sphaera of Ptolemaei map.
.C. 1400
12
Map of the World, Bologna edition of Ptolemy Geographia .C. 1482
13
Ptolemy of the Middle East.Ptolemy of the Middle East .C. 1482
14
Koeln_map_of_Middle_East_1584 Koeln map of Middle East
.C. 1484
15
Arabia_Persian_Gulf_and_Insia_Ocean_1484*
Persian Gulf and Arabia from Claudius Ptolemaeus, Cosmographia,
Jacobus Angelus interpres (Bliothèque nationale de France).C. 1484
16
Arabia_and_Levant_1484Arabia and Levandt from Claudius Ptolemaeus,
Cosmographia, Jacobus Angelus interpres (Bliothèque nationale de France).C. 1484
17
Quater_of_Asia_1486* Quater of Asia..C. 1486
18
Incunabula_world_map_by_Hartmann_Schedel_1493
German Map of the World by Hartmann Schedel .C. 1493
19
Danckerts Map of Asia 1500Danckerts Map of Asia..C. 1500
20
Ptolemys_world_map_15th_century..Ptolemy's world map (Persicus Sinus).C. 15th century
21
Alberto_Cantino_World_MapWorld Map by Alberto Cantino.C. 1502
22
J_Pentiusde_Leucho_mapWorld map from Ptolemy, Geographia. Venice: J.Pentius de Leucho .C. 1511
23
QUINTA_ASIE_TABULA_1513 Qunita Unita Asie Tabula..C. 1513
24
Pietro_Coppo_map_of_AsiaPietro Coppo map of Asia. .C. 1520
25
Persian_Gulf.Map denoting Sinus Persicus..C. 1531
26
French map of Persian Gulf.C. 1540
27
Swiss_map_PG_1540_Basel.Swiss map based on Ptolemy's Geographia.C. 1540
28
Persian_Gulf_Italian_Map1548. Giacomo Gastaldi's map denoted by
cartographic historian Gerald Tibbetts as the first "modern" map of the area, denoting 'Golpho de Persia'.circa 1548
29
Asia_by_Sebastian_Munster_1545Asia by Sebastian Munster.C. 1545
30
Arabia_Felice_Nuova_Tavola_1574Italian map of Arabia Felice Nuova Tavola.C. 1574
31
Ptolemy_PG_1578.Gerhard Mercator's atlas production from Ptolemy's Geographia,
depicting Sinus Arabicus (for Red Sea) and Persicus Sinus (Persian Gulf).C. 1578
32
Ortelius_Map_1580Map by Abraham Ortelius using the term "Persicus" (MAR MESENDIN ol. Sinus Persicus).C. 1580
33
1588_Persian_Gulf_Map.Map by Sebastian Munster.C. 1588
34
Asia_by_Heinrich_Bunting.Asia by Heinrich Bunting.C. 1590
35
Jan_Huygen_Van_LinschotenMap of Asia by Jan Huygen Van Linschoten.C. 1596
36
German_map_Matthaus.German map.C. 1598
37
16th_c_PG_ufl.Map of Near East.C. 16th century
38
Iran_Map_Hondius.Map by Dutch map maker Jodocus Hondius.C. 1610
39
Persici_Sive_Sophorum_Regni_Typus_by_Abraham_Ortelius Abraham Ortelius Map of Persia.C. 1612
40
Near_East_William_Hole English map of the Near East by William Hole.C. 1614
41
Italian Map of Asia (Table VII) by P. and F. Glignani, Paduaca.C. 1621
43
French_Map_of_Persia_and_independant_terretoriesPersia & Independent Tartarie.C. 1623
44
John_Speed_Map_of_AsiaJohn Speed Map of Asia.C. 1626
45
Posidonius_map_of_the_world_by_Petrus_Bertius__Melchior_Tavernier_1628
Greek map of the world by Petrus Bertius & Melchior Tavernier (Sinus Persicus).C. 1628
46
Ancient Mesopot French map of Ancient Mesopotamia,.C. 1631
47
Populi Persarum Arabes 1675Populi Persarum Arabes.C. 1675
48
Asia_by_Gerhard_Mercator_1695Asia by Gerhard Mercator.C. 1695
49
Egypt__North_Africa_showing_Ewd_sea_as_the_Persian_Sea_1696*
German Map of Egypt & North Africa showing 'Red sea' as the 'Arabisch Sinus Pars' .C. 1696
50
Map_of_Persian_Gulf_by_John_Thornton_1699English map of Persian Gulf by John Thornton.C. 1699
51
PersianGulf_Jansson.Jan Jansson's map of the Persian Gulf.C. 17th century
52
Periplus_Latin_Map Periplus Latin Map.C. 17th century
53
Spanish_Map_of_the_Europepanish Map of the Europe.C. 1700
54
Italian_Map_of_AfricaItalian Map of Africa.C. 1700
55
Italian_Map_of_Asia_the_Persian_Gulf_and_Sea_.C. 1700
Italian Map of Asia the Persian Gulf and the Persian Sea (Oman Sea)
56
Near_East_and_Europe_by_Guillaume_de_Lisle_.C. 1709
French map of the Near East and Europe by Guillaume de L'isle
57
Das Reich der Perser und der PorthenA German Map of the Parthian Empire, Frankfurt.C. 1719
58
Persia_Weigel_Christoph.C. 1719 Persia by Christoph Weigel
59
Parthia by Allain Manesson Mallet.C. 1719
60
Iran_e_Bozorg2World Map.C. 1719
61
Persia_Homann_Johann_Baptist.C. 1720Persia Homann, Johann Baptist
62
Italian map of Africa with Persian Gulf and teh Persian Sea (Oman Sea) by Paolo Petrina of Napoli .C. 1722
63
Africa_by_John_Senex_1728Africa by John Senex.C. 1728
64
Seutte_Persia_and_Arabia_Geographicus_1730Seutter Persia and Arabia Geographicus.C. 1730
65
Persia_by_Mattheus_Seutter.C. 1730 Persia by Mattheus Seutter
66
Ottoman_Map_by_Heirs_Homann_Nuremberg_.C. 1737
German map of Ottoman Empire by Heirs Homann, Nuremberg
67
Persian_Gulf_French_map1740French map of Persia.C. 1740
68
Seutter_Map_of_Persia_and_Middle_East_1740Seutter Map of Persia and Middle East.C. 1740
69
Persia_By_Ch-Cellarius_1747 Persia By Ch-Cellarius (and the enlarged section) .C. 1747
70
Asia_secundum_legitimas_Projectionis_Stereographicae_1744*
British_Map_of_Asia_1808_Persia__section
Asia secundum legitimas Projectionis Stereographicae -
In this map the Persian Gulf & the Persian Sea mentioned for(Arab Sea).C. 1744
71
Persia Emanuel Bowen 1747 Emanuel Bowen map of Iran (Library of Congress, USA).C. 1747
72
Persian_Gulf_map_van_keulen_1753Iran and Persian Gulf by Van Keulen.C. 1753
73
Ottoman_Empire_by_L._Euler_C.1753_Berlin Ottoman Empire by L. Euler, Berlin
- The Persian Gulf & the Persian Sea (arab Sea)
74
French_Map_of_Arabia_1772French Map of Arabia.C. 1772
75
Near_East_Thomas_Jefferys_1754Near East Thomas Jefferys.C. 1754
76
Indian_Ocean_by_Nicolaus_Bellin_1758German map of Indian Ocean by Nicolaus Bellin.C. 1758
77
Middle-East_Vaugondy_1767Middle-East Vaugondy.C. 1767
78
English_map_of_Persia_by_John_Gibson_1770English map of Persia by John Gibson.C. 1770
79
Carte_De_LArabia__Paris_1771Carte De L'Arabia, Paris
.C. 1771
80
Marine_Map_of_Asia_Paris_1780Marine Map of Asia, Paris .C. 1780
81
Persia_and_Garden_Eden_by_Thomas_Bowen_1780
English map of Persia and the Garden Eden by Thomas Bowen .C. 1780
82
Persian_and_Northern_Asia_by_M_Bonne_1780Persian and Northern Asia by M Bonne.C. 1780
83
French_map_of_Kingdom_of_Persia_by_M._Bonne_1780French map of Kingdom of Persia by M. Bonne.C. 1780
84
Italian_map_of_the_Empire_of_Persia_by_Antonio_Zatta_1784Italian map of the Empire of Persia by Antonio Zatta.C. 1784
85
Tuquie_dAsie_et_Perse_Turkey__Persia_1795French map of Turkey & Persia,.C. 1795
86
Map_of_Persia_and_the_Persian_Gulf_1797Map of Persia and the Persian Gulf.C. 1797
87
German_map_of_Persia_by_.C.G_Reichard_1804German map of Persia by .C.G. Reichard.C. 1804
88
Asia_Mollo_Tranquillo__1807Asia Mollo, Tranquillo.C. 1807
89
British_Map_of_Asia_1808.British Map of Asia_1808_Persia _sectionA British map and the enlarged section.C. 1808
90
Persia_including_PersianGulf_1811Persia (including the Persian Gulf's Arab states).C. 1811
91
IranPersianGulf_1820Map by Universal Dictionary of Arts, Sciences, and Literature by Abraham Rees.C. 1820
92
Drury map of Persia 1822Drury Map of Persia.C. 1822
93
Ancient_Persia_S._D._U._K_1831Ancient Persia S. D. U. K..C. 1831
94
Berghaus_Physical_map_of_Indian_Ocean_1840Berghaus' Physical map of Indian Ocean.C. 1840
95
Berghaus_Physikalischer_Atlas_C.1841Berghaus' Physikalischer Atlas.
96
British Map of the Persian Gulf .C.1822British Map of the Persian Gulf
97
Berghaus_map_of_Europe_and_Asia_1842Berghaus' map of Europe and Asia.C. 1842
98
- & .C. Walker Detailed engraved map of Arabia 1843.British Detailed engraved map by J. & .C. Walker.C. 1843
99
Persia A K Johnston National Atlas 1843British Map of Persia by A K Johnston National Atlas.C. 1843
100
Berghaus_Physikalischer_Atlas5.C.1846Berghaus' Physikalischer Atlas
101
Berghaus_Physikalischer_Atlas4_C.1847Berghaus' Physikalischer Atlas
102
Hildburghausen_Meyer_1848Hildburghausen Meyer .C.1848_Persia SectionHildburghausen Meyer Map of Asia
- British_map_of_Persia__Kabul_by_Philip GeorgeandSon.C.1852
British map of Persia & Kabul by Philip George and Son
104
JohnTallis_Persia.C.1851.Map of Persia, by John Tallis
105
.British_School_Atlas.British School Atlas.C. 1852
106
English_Historical_Textbook_and_Atlas_of_Biblical_Geography_by_Coleman_1854English Historical Textbook and Atlas of Biblical Geography by Coleman.C. 1854
107
Coltons Persia and Arabia Map.C. 1855Coltons Map of Persia & Arabia
108
handbookbible- C.1870Handbook of Bivle Geography Britain
109
the-admiralty_nories-navigation.C.1877_indian-oceanThe British Admiralty Nories Navigation Map of Indian Ocean.C. 1882
110
Persia_1900British Map of the Western Asia.C. 1900
111
Atlas of Ancient and Classical Geography, Samuel Butler.C. 1907
112
Official_British_Map_of_Asia_1914British Map of Asia.C. 1914
113
Cairo1908_PG_map Egyptian Map Africa showing Persian Gulf (al-Khalija al-'Ajam = Iranian Gulf).C. 1908
114
Cairo1910_PG_mapEgyptian Map of Persian Gulf (al-Khalija al-'Ajam - Iranian Gulf) .C. 1910
115
ancient-middle-east_by_vidal-lablache_atlas-general-histoire-et-geographie.C.1912 Vidal Lablache Atlas's Ancient Middle-East
116 sundaytimesMap.1913Published in "The Sunday Times" (London)
117
Persian_Gulf_by_British_Government_Handbook_on_ArabiaThe British Government Handbook on Arabia.C. 1919
118
london geographical nstitute 1920The Peoples Atlas, London Geographical Institute.C. 1920
119 Saudi_map_of_Persian_gulf_1952_Saudi_AramcoA Saudi ARAMCO map showing the Persian Gulf .C. 1952
120
PersianGulfMap_cairo1965 map of Middle East by Sobhi Abdul-Karim, Cairo.C. 1965
121 Persian-Gulf-Dubai-mus_19th C. A defaced historical map of the Persian Gulf in Dubai museum. The word Persian was removed.
***Maps by following cartographer have also described Persian Gulf:
- Maps by Paolo del Pozzo Toscanelli
- Maps by Francisco Rosselli
- Maps by Juan de la Cosa
- Martin Waldseemuler
- Sebastian Munster
- Jamoco Gastaldi
- Girolamo Ruscelli
- Giovanni Antonio Magini
- Gerard Mercator
- Abraham Ortelius
- Frederick de Wit
- Nicolas Jansz. Visscher
- Christophoro Weigelio
- Guillaume de L> Isle
- Emanuel Bowen
- 26Rigobert Bonne
- Isaac Tirion
- Tobias Conradi Lotteri
- Fielding Jr.Lucas
- Adam Olearius
- Engelbert Kaempfer
- Carsten Niehbur
- Petrus Bertius
- Pieter Van der Aa
- Jean Baptiste Bourguignon d>Anville
- Guillaume Nicolas Delahaye
- Aaron Arrowsmith
- Captain Ritchie
- Bartholomew R.B.
- Captain James Horseburgh
- A. Garnier
- George Percy Badger
- James Neele
.jpg)
وقد افتتح هذا المتحف برعایه “المؤسسه الجغرافیه” عام ۲۰۰۷ وهو مفتوح للجمیع.
هاتف الاتصال : ۸۸۴۵۹۸۹۱ – ۰۰۹۸۲۱
العنوان : ایران – طهران – شارع شریعتی ، شارع معلم ، المؤسسه الجغرافیه
مقر الاحتفاظ ، متحف المؤسسه الجغرافیه
الاسم الکامل هو خریطه الخلیج الفارسی والذی حدد فی قلب الخریطه بعنوان PERSIAN GULF
واضع الخریطه ، دائره المسح بالجیش الامریکی (الفرع الهندسی)
عام ۱۹۶۲ میلادی
مقر الاحتفاظ ، متحف المؤسسه الجغرافیه
وقد سجل اسم الخلیج الفارسی فی هذه الخریطه بعنوان PERSIAN GULF
واضع الخریطه ، القسم الجغرافی بالجمعیه الجغرافیه الوطنیه للولایات المتحده الامریکیه للافاده منها فی مجله National Geography (واشنطن دی سی)
عام ۱۹۴۲ میلادی
مقر الاحتفاظ ، متحف المؤسسه الجغرافیه
واضع الخریطه ، القسم الجغرافی بالجمعیه الجغرافیه الوطنیه للولایات المتحده الامریکیه للافاده منها فی مجله Natioal Geography (واشنطن دی سی)
عام ۱۹۵۰ میلادی
مقر الاحتفاظ ، متحف المؤسسه الجغرافیه
تم تسجیل اسم الخلیج الفارسی فی هذه الخریطه بعنوان PERSIAN GULF
واضع الخریطه ، شرکه هومن اربی (ورثه جون بابتیست هومن) المانیا
عام ۱۸۰۲ میلادی
مقر الاحتفاظ ، متحف المؤسسه الجغرافیه
وتم فی هذه الخریطه ذکر الخلیج الفارسی بعنوان PERSISCHER MEERBUSEN
واضع الخریطه : منسوب الى بطلیموس
سنه الرسم غیر محدده
مقر الاحتفاظ ، متحف المؤسسه الجغرافیه
وکما یشاهد فی الخریطه فانه تمت تسمیه بحر الجنوب او ارض بارس باسم SINS PERSIVS وهو الخلیج الفارسی کما تم اعتبار الجزر الواقعه فی هذا البحر بانها جزء من ارض بارس
واضع الخریطه : فرنسا
سنه الرسم غیر محدده
مقر الاحتفاظ ، متحف المؤسسه الجغرافیه
وتم تسجیل اسم الخلیج الفارسی فی هذه الخریطه بعنوان Golfe Persique وهو اللفظ الفرنسی للخلیج الفارسی
واضع الخریطه ، جون کری
سنه الرسم ، ۱۸۱۹ میلادی ، بریطانیا
مقر الاحتفاظ ، متحف المؤسسه الجغرافیه
وتم تسجیل اسم الخلیج الفارسی فی هذه الخریطه بعنوان PERSIAN GULF
واضع الخریطه ، دائره المسح فی الولایات المتحده الامریکیه
عام ۱۹۵۹ میلادی
مقر الاحتفاظ ، متحف المؤسسه الجغرافیه
تم تسجیل اسم الخلیج الفارسی فی هذه الخریطه بعنوان PERSIAN GULF
واضع الخریطه : مرکز اعداد الخرائط الدفاعیه لوکاله الهواء فضاء الامریکیه
سنه الرسم ، ۱۹۵۷ میلادی (اعاده النظر فی عام ۱۹۷۲ میلادی)
مقر الاحتفاظ ، متحف المؤسسه الجغرافیه
تم تسجیل اسم الخلیج الفارسی فی هذه الخریطه بعنوان PERSIAN GULF
واضع الخریطه : جی فورست
سنه الرسم غیر محدده (فرنسا)
مقر الاحتفاظ ، متحف المؤسسه الجغرافیه
تم تسجیل اسم الخلیج الفارسی فی هذه الخریطه بعنوان G.Persique
واضع الخریطه : مرکز المعلومات وخرائط الطیران بالقوه الجویه للولایات المتحده الامریکیه
سنه الرسم ، ۱۹۵۳ میلادی (اعاده النظر فی عام ۱۹۵۶ میلادی) امریکا
مقر الاحتفاظ ، متحف المؤسسه الجغرافیه
تم تسجیل اسم الخلیج الفارسی فی هذه الخریطه بعنوان PERSIAN GULF
بطلیموس (۸۷ – ۱۵۰ میلادی)
واضع الخریطه : منسوب الى بطلیموس
سنه الرسم : ۱۵۲۰ میلادی على شکل کلیشیه خشبیه
مقر الاحتفاظ ، متحف المؤسسه الجغرافیه
تم تسجیل اسم الخلیج الفارسی فی هذه الخریطه بعنوان suuis Persian
LIST OF SOME EARLY MAPS WHICH HAD MENTIONED THE PERIAN GULF
.jpg)
2.2. The Origin of Attempts to Distort the Name of Persian Gulf
According to many relevant studies, the origin of distortion dates back to 1960s, but whether the government of Britain or Arab countries first began the story requires further discussion. A group of researchers believe some Arab countries began to use the forged name with the spread of Pan-Arabism. The Arabism ideology seeks to unite the Arab world by certain principles and policies. Some other assert that Charles Belgrave and Roderick Oven, the British government agents, used the forged name “Arabic Gulf” in their books for the first time, after which it spread to Arab countries, and we do not encounter such name even in the books or writings of the Arabs, except for some historians and geographers calling the Red Sea “Arabian Gulf . In 1958, Abd al-Karim Qasim staged a coup in Iraq and claimed to be the leader of the Arab world, so he needed to propound the theory of foreign enemy in order to attract the Arab nations’ interest and attention. At that time, the Arab world led by the Egyptian colonel Gamal Abdel Nasser was engaged in a conflict with Israel [6]. By changing the names “Persian Gulf” and “Khuzestan”, Abdel Nasser resolved to introduce Iran as a new enemy to the Arab world in order to direct attention from Cairo to Bagdad. He used this political game with history and geography as a pretext for creating a division between the Arab nations and Iran. However, since the coup and violent policies of the colonels of Bagdad failed to interest Arabs, Abd al-Karim Qasim’s propaganda found no place among them too . Not only Kuwait, which used to be under the fear and political pressure of Bagdad, signed its contract of independence with Britain as “Al-khalij Al-Farsi” (Persian Gulf) in 1958, there have also been tens of deeds and maps published in Iraq which used the true name “Persian Gulf”
THE MAJOR REASONS FOR DISTORTING THE NAME “PERSIAN GULF”
3.1. The Disputes Between Iranians and Arabs Throughout History
The relations between Iranians and Arabs before and after the advent of Islam clearly explain the background of these disputes. Before the rise of Islam and in the period of Jahiliyya2, the Arabs, deprived of any civilization, were either subordinate to the Persian Empire or Roman Empire. As Islam spread all over the region and Iran and brought bliss and honor to the Arabs, the behavior of Arab states, contrary to the true teachings and principles of Islam, was based on race and ethnicity. However, Iranians soon retrieved their independence and honor. Despite some interactions between Iranians and Arabs at the dawn of Islam, they had conflicts too, for which the racial discrimination policies of Umayyad Caliphs were the main reasons. The Umayyad Regime was founded in AD 661 and lasted for near a century. They revived the ethnic and racial privileges, formerly annulled by the teachings of Islam. The Umayyad Caliphs discriminated against non-Arabs, especially Iranians. Iranians’ strong feeling of affection and devotion towards Ali ibn Abi Talib3 led to such discrimination. Despite the fact that Iranians warmly welcomed Islam, the aforementioned discrimination and unfair practice of Umayyad Caliphs triggered the conflicts.
***. The Arab Extremists; an Escape from Identity Crisis
A part of this refers to the historical disputes between the two sides and the rest is related to the Arabs’ historical identity. The extremist groups consider forging a historical identity as the easiest way to escape from lack of a valuable identity. The Arab extremists’ attempts to distort the name “Persian Gulf” are rooted in an identity crisis. Lack of civilization before Islam is a notable example. As mentioned in the Quran1, in pre-Islamic Arabia, people used to bury alive female newborn infants because a daughter was considered a disgrace to the family. The Third Arab-Israeli War in 1967 which led to Israel’s decisive victory and also the unfavorable image of Arabs presented by Hollywood made them frantically endeavor to revive their lost reputation in the world.
3.3. Non-Arab Self-Seeking Institutes
There are generally other groups that foment discord and benefit from it. Obviously, the project of distortion has been funded by petrodollars of Arab countries. A number of Western research institutes seized the opportunity and encouraged the regional Arab countries to advance the project. By providing forged deeds about the Persian Gulf, the aforementioned institutes would take a large amount of money. Two of the noblest sciences, law and history, were manipulated in order to distort the name “Persian Gulf”, hence, historians and legal experts were the most serious objectors to this distortion. In their view, invasion of a nation’s history means a moral transgression and signifies downfall of values [8].
3.4. The Arab world’s Concern about Iran
In recent years, Iran’s effort to achieve the nuclear energy has caused some kind of fear in the Arab countries bordering the Persian Gulf which is the result of anti-Iran propaganda spread by the West, especially the US. Despite all peacemaking efforts of Iranian religious officials and politicians, Arab states are still concerned about Iran’s power. Not only will this concern be assuaged, it might deteriorate as well by orations or statements. All negative points contained in the history of Islam or even before Islam such as being Arab or non-Arab, Shiite or Sunni, etc. have been fixed in their mind and constantly provoked by the colonialist powers. This fear of Iran, albeit delusional, has caused an alliance in the Arab nations and consequently the iterative claims over the ownership of the Islands Abu Musa, Greater Tunb, and Lesser Tunb and also distortion of the name Persian Gulf have been a major issue in the Middle East.
National Persian Gulf Day is a very significant day for the Iranian people and it is celebrated annually on April 30th.
It has taken place every year since 2005, and is marked with various rituals all over Iran, especially in the coastal cities of the Persian Gulf. The Persian Gulf, in Western Asia, is an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran (Persia) and the Arabian Peninsula.
According to the book Documents on the Persian Gulf’s name : the eternal heritage of ancient time the term Persian Gulf and its equivalents have been used constantly since 400 BC, but in 1964 the Arab league ratified a change of the name the Arabian Gulf.
Apparently, this change was not accepted by some Arab countries. After the Iran-Iraq war, the decision was realized. The act annoyed Iran/Iranians, especially when the Arabs tried to use the name Arabian Gulf in the English mass media. While historical documents indicat that the waterway has always been referred to as the ‘Persian Gulf,’ certain Arab states have mounted efforts to remove ‘Persian’ from the name of the waterway. After many meetings and seminars by the NGOs and the geographers of Iran asking the government to preserve the heritage name of the Persian gulf, finally Iran, in 2004 officially designated April 30 as the “National Persian Gulf Day”, since the date coincides with the anniversary of Shah Abbas,’ a successful military campaign against the Portuguese navy in the Persian Gulf, driving the Portuguese colonial forces out of the Strait of Hormuz in the Capture of Ormuz (1622).
The decision was taken by the High Council of Cultural Revolution, presided over by former President Mohammad Khatami, the council mentioned the campaign launched recently by certain Arab states to rename Persian Gulf as the drive behind the decision.
In 1514, the Portuguese captured Hormuz and built a fort. For more than a century the island remained Portuguese, but they were routed and forced to withdraw after 100 years by the Iranian forces. The Portuguese then lost all their colonial lands in east Africa and were forced back to Mozambique.
April 29 -30 is celebrated in Iran as ‘Persian Gulf Day’. Iranians care so much about the Persian Gulf , they dedicate April 29 to it in official calendar. In fact, the Persian Gulf is not just a body of water, but part of the culture, history and identity of Iranians and the whole region.
The historical, geographical and commercial position of the Persian Gulf, a place for all living civilizations to live and interact, makes it special to celebrate a day for; a day for all the Iranians to have a short opportunity to defend the historical and authentic truth of the Persian Gulf. This day is the anniversary of forcing out the Portuguese navy of the Strait of Hormuz in the Capture of Ormuz.
- The Persian Gulf is a valuable treasure, containing half of the world’s oil reserves, with a unique geographical location that profiteers are always plotting to dominate this regional and global economic highway. Geographical Position and Naming Issue: according to the book" Documents on the Persian Gulf's name The Persian Gulf is a name since 3000 years mentioned in books ,maps and artistic and archeological sites.
While today some regional elements making extensive efforts to use and establish a fake name (Arab Gulf) for the Persian Gulf which lacks historical citations and logical arguments. the United Nations has stated that it does not know any other name other than the Persian Gulf title.
The Persian Gulf, as a water and sea route, has been of great value since the dawn of history and has a history of several thousand years as a clash of ancient civilizations.
Historically, the shores of the P.gulf and the rivers that flowed into it have been the site of the first human civilisations. By studying the history of the Persian Gulf, you can go to sea with ancient fishermen; hunt pearls from Qeshm Island, go to Mesopotamia and dig out the ancient inscriptions of Cyrus; listen to historical stories of the atrocities committed by colonialists on the island of Hormuz, and hear the story of the outbreak of bloody wars and the pirates.
So, for Iranians, the Persian Gulf is not just a sea, but part of history, identity and national heritage. the Persian Gulf is a symbol of civilisation, culture and history that connect the nations of the region. Therefore, now all the countries in the region have a responsibility to preserve the historical heritage of this region in the same historical and original way. Some civilisations like Elamites and Persians date back more than 7,000 years, while others do not exceed a few decades; however, the historical character, originality and dignity of each country requires that it be proud of its resources and not be greedy about the cultural, geographical and ancient resources of others. No country is allowed to create a false identity for itself by distorting history, overturning the facts and stealing the cultural heritage of others.
The same importance of identical and strategic importance of the Persian Gulf has caused some racist individuals and organisations to use fake names for this gulf in the last few decades in order to be honoured by attributing it to them. But researchers, lawyers, historians and lovers of the Persian Gulf have prevented this with the help of the United Nations. All ancient geographical documents and maps in different languages such as Persian, Arabic, Spanish, etc. have referred to that gulf as the “Persian Gulf”. Thus, the distortion of its name is nothing but the blatant denial of a historical truth. The United Nations, citing ancient maps and texts, has been emphasizing the name of the Persian Gulf since 1980 with the issuance of various resolutions and statements.
The most important thing that has made the Persian Gulf extremely significant is the existence of natural resources, especially oil, so that the name of the Persian Gulf has become equal to oil and gas.
A major factor that makes the Persian Gulf oil and gas so vital to the United States, Western Europe, and Japan is the great difficulty in replacing the region’s imported oil and gas with resources.
The Persian Gulf region has the one of the largest oil and Gas reserves.
The Persian Gulf offers a unique model of a geopolitical region among the regions that exist in the part known as the Middle East, as separate and distinct geopolitical regions. The region includes nations that are culturally diverse but coordinated politically, strategically, and economically.
The gulf contains countless valuable marine resources and has valuable animal and plant species, the preservation of which requires the efforts of littoral states. The gulf is also an important international waterway, with its privileged location between the three continents of Europe, Asia and Africa, making it a highway for maritime trade in the region and the world.
All the historical, cultural-identical, economic, geo-economic and geopolitical aspects of the Persian Gulf make it doubly important to maintain the security of this gulf for the whole region.
https://www.isna.ir/news/97021006028/
- RECOMMENDATIONS Although there are well-founded books about the history of Persian Gulf, a very small number of them were translated into foreign languages. The authors suggest that the books about the Persian Gulf containing historical information, maps and deeds should be translated into the official languages of the United Nations (Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, and Spanish). In order to do this, Iran’s Supreme Cultural Revolution Council must provide the active support, because one of its goals is to formulate and advance policies and strategic plans of the country in different cultural issues.
So far, dozens of prominent figures in the Arab world have admitted in separate articles that:
" Until the reign of Abdel Nasser in Egypt, the word 'Arab Gulf' cannot be found in any Arabic documents or oral literature, so changing the original and historical name of the Persian Gulf is incorrect."
Among them: Abdul Hadi Al-Tazi, Abdullah Ibn Kran, Abdul Khaliq Al-Janabi
bi, Abdul Moneim Saeed, Abdul Rahman Rashid, Yusuf Al-Qaradawi, Majdi Omar, Saad Ibn Tufla, Ahmad Al-Sarraf, Salah Al Sayer, Al-Mubarak Ibn Abdul Aziz- Ali
Hamidan. Nejah M.Ali -Hozan Qaso and
 ....
....
Excerpts from the Book”:
Documents on the Persian Gulf's name by Dr.Mohammad Ajam . parssea.org
REFERENCES
Documents on the Persian Gulf's name the eternal heritage ancient time by Dr.Ajam
M. Ajam, (2011a), Persian Gulf in the Arab Treaties and International Law, Journal of History & Geography, 155, 2
M. Ajam, (2011b), Persian Gulf in the Arab Treaties and International Law, Journal of History & Geography, 155, 7
United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names (2006), Historical Geographical and Legal Validity of the Name: Persian Gulf, available at:
http://unstats.un.org/unsd/geoinfo/UNGEGN/docs/23-gegn/wp/gegn23wp61.pdf

Documents on the Persian Gulf's name the eternal heritage ancient time is a book and atlas written and compiled by Dr. M. Ajam.
published , 2004 and 2009
http://realiran.org/april-30th-national-persian-gulf-day/
http://www.hcot.ir/Ketab/E-Magazine/MahFiles/T155.pdf
http://www.persiangulfstudies.com/fa/index.asp?p=pages&ID=774&Sub=619
https://twitter.com/IraninJapan/status/1199918736242688000
https://b2n.ir/052813 1388 تهران کتاب اسناد نام خلیج فارس، میراثی کهن و جاودان نویسنده دکتر محمد عجم
https://b2n.ir/882477 تحریف نام خلیج فارس
https://japan.mfa.gov.ir/portal/newsview/46003
https://japan.mfa.gov.ir/portal/newsview/46001
https://japan.mfa.gov.ir/en/NewsView/569062/The-persian-gulf-Exhibition-of-Historical-Documents
- https://japan.mfa.gov.ir/portal/newsview/46003
- https://japan.mfa.gov.ir/portal/newsview/46001
- https://japan.mfa.gov.ir/en/NewsView/569062/The-persian-gulf-Exhibition-of-Historical-Documents
- https://japan.mfa.gov.ir/en/newsview/536034
- https://japan.mfa.gov.ir/en/newsview/536033
- UNGEGN: A glance at the Historical, Geographical and Legal Validity of the term : Persian Gulf
- https://www.webcitation.org/6PuCsAOso
نوشته دکتر محمد عجم ، بحر فارس و تفسیر قرانی و حدیث پیامبر
https://japan.mfa.gov.ir/jp/newsview/548279 NATIONAL PG day
https://japan.mfa.gov.ir/en/newsview/536033
https://www.aparat.com/v/sbfoF
ویدیوی گفتگوی شهر آرا با دکتر عجم 98
https://web.archive.org/web/20201112214718/http://parssea.org/?m=202007
معرفی کتاب به انگلیسی
https://web.archive.org/web/20160530204556/http://www.farsnews.com/printable.php?nn=8302020084
همایش دوم اردیبهشت 83
https://kids.kiddle.co/Documents_on_the_Persian_Gulf%27s_name
https://kids.kiddle.co/Image:Documents_on_the_Persian_Gulf%27s_name.gif
https://kids.kiddle.co/images/1/12/Documents_on_the_Persian_Gulf%27s_name.gif
https://web.archive.org/web/20200220031503/http://parssea.org/?p=724
نقشههای خلیج فارس
https://web.archive.org/web/20131203005112/http://parssea.org/?p=1338
دفاع حقوقی خلیج فارس
https://web.archive.org/web/20210117131448/http://catdir.loc.gov/catdir/toc/fy11pdf02/2010344035.pdf
https://www.magiran.com/author/%d9%85%d8%ad%d9%85%d8%af%20%d8%b9%d8%ac%d9%85
مقالات عجم
به مناسبت 10 اردیبهشت؛ روز ملی خلیج فارس
http://www.mediafire.com/file/th9u85dy9igaw36/Khalij_fars.pdf/file
نسخه پی دی اف آنلاین کتاب رایگان
https://www.farsnews.ir/news/8503160416%20%20%20%20/جزایر-سه-گانه-خلیج-فارس-و-داستان-بحرین-
http://fna.ir/
http://ensani.ir/fa/article/217848/خلیج-فارس-در-قراردادهای-عربی-و-معاهدات-و-حقوق-بین-المللی
https://web.archive.org/web/20200629201336/http://shahraraonline.ir/final/site/news-content.php/73526?id=73526
گفتگو با نخستین پیشنهاد دهنده روز ملی خلیج فارس که اسناد و نقشههای تاریخی زیادی را در تایید این عنوان جمعآوری کرد؛
نقش «عجم» بر نقشه
https://www.hamshahrionline.ir/news/106180/نام-خلیج-فارس-در-قراردادها-و-معاهدات-منطقه-ای-و-بین-المللی
نام خ در قراردادهای بین المللی
https://www.hamshahrionline.ir/xVdX
مقاله دکتر عنایتی و عجم
https://www.isna.ir/news/97021005937/
نام خلیج فارس در قراردادها و معاهدات منطقه ای و بین المللی
محمد عجم
https://www.magiran.com/paper/2075411
https://sanad.um.ac.ir/index.php?option=com_mag&view=htmlpage&id=628&hp=1430&lang=fa
علل تحریف خلیج فارس
عنوان نشریه : فصلنامه سیمرغ
شماره نشریه : 7
تاریخ انتشار : دوشنبه, ۸ خرداد ۱۳۹۶
صاحب امتیاز : کانون فرهنگ و ایران شناسی
https://khabarban. com/18323029/
نسخه آرشیوی دریای پارس
https://www.webcitation.org/6PuCsAOso
نسخه آرشیوی دریای پارس
https://web.archive.org/web/20150310195346/http://zoodi.com/Persian-Gulf/2-naming-p-gulf.htm
/Persian-Gulf-Hamayesh/ASNAD-NAGHSHE-TARIKHI/main-Maps-Docs-Irane7000saale.pdf
شهر ارا : شرح چگونگی ثبت روز ملی خلیج فارس در گفتگو با محمد عجم
https://web.archive.org/web/20181015042136/http://shahraraonline.ir/final/site/news-content.php/73526?id=73526
https://web.archive.org/web/20160404121937/http://parssea.persianblog.ir/post/1/
سال 1381
https://web.archive.org/web/20140108164611/http://ajam1.persianblog.ir/
https://web.archive.org/web/20160329001026/http://parssea.persianblog.ir/1381/10/
https://web.archive.org/web/20120124012018/http://farsi-arabi.persianblog.ir/
https://web.archive.org/web/20120423231748/http://bahrefars.persianblog.ir/
https://web.archive.org/web/20160404121937/http://parssea.persianblog.ir/post/1/
کتاب خلیج فارس به زبان عربی
https://web.archive.org/web/20120511010557/http://farsi-arabi.persianblog.ir/
https://web.archive.org/web/20201112214718/http://parssea.org/?m=202007
Introducing a book and Atlas
https://web.archive.org/web/20120205062033/http://www.persiangulfonline.org/asp/forum1/display.asp?messageNo=1&threadID=193
https://web.archive.org/web/20120205062023/http://www.persiangulfonline.org/takeaction/pr012805.htm
https://web.archive.org/web/20190407210545/http://parssea.org/?p=117
https://web.archive.org/web/20190331065604/http://parssea.org/?p=973
https://web.archive.org/web/20200618103154/http://parssea.org/?p=1363
کتابهای خلیج فارس شناسی
https://web.archive.org/web/20200620041041/http://parssea.org/?p=1338
دفاع حقوقی ایرانیان از نام خلیج فارس
https://web.archive.org/web/20181008115547/http://parssea.org/?p=800
جنگهای ایران و استعمار شوم پرتغال در خلیج فارس
https://web.archive.org/web/20160304232056/http://parssea.org/?p=4053
https://japan.mfa.gov.ir/en/newsview/536033
https://www.aparat.com/v/sbfoF
ویدیوی گفتگوی شهر آرا با دکتر عجم 98
https://web.archive.org/web/20201112214718/http://parssea.org/?m=202007
معرفی کتاب به انگلیسی
https://web.archive.org/web/20160530204556/http://www.farsnews.com/printable.php?nn=8302020084
همایش دوم اردیبهشت 83
https://kids.kiddle.co/Documents_on_the_Persian_Gulf%27s_name
https://kids.kiddle.co/Image:Documents_on_the_Persian_Gulf%27s_name.gif
https://kids.kiddle.co/images/1/12/Documents_on_the_Persian_Gulf%27s_name.gif
https://web.archive.org/web/20200220031503/http://parssea.org/?p=724
نقشههای خلیج فارس
https://web.archive.org/web/20131203005112/http://parssea.org/?p=1338
دفاع حقوقی خلیج فارس
http://www.webcitation.org/6PuCsAOso
https://web.archive.org/web/20210117131448/http://catdir.loc.gov/catdir/toc/fy11pdf02/2010344035.pdf
https://www.magiran.com/author/%d9%85%d8%ad%d9%85%d8%af%20%d8%b9%d8%ac%d9%85
مقالات عجم
به مناسبت 10 اردیبهشت؛ روز ملی خلیج فارس
http://www.sayeh-news.com/fa/Main/Detail/46037/
به مناسبت 10 اردیبهشت؛ روز ملی خلیج فارس
http://www.mediafire.com/file/th9u85dy9igaw36/Khalij_fars.pdf/file
نسخه پی دی اف آنلاین کتاب رایگان
https://www.farsnews.ir/news/8503160416%20%20%20%20/جزایر-سه-گانه-خلیج-فارس-و-داستان-بحرین-
http://fna.ir/
http://ensani.ir/fa/article/217848/خلیج-فارس-در-قراردادهای-عربی-و-معاهدات-و-حقوق-بین-المللی
https://web.archive.org/web/20200629201336/http://shahraraonline.ir/final/site/news-content.php/73526?id=73526
گفتگو با نخستین پیشنهاد دهنده روز ملی خلیج فارس که اسناد و نقشههای تاریخی زیادی را در تایید این عنوان جمعآوری کرد؛
نقش «عجم» بر نقشه
https://www.hamshahrionline.ir/news/106180/نام-خلیج-فارس-در-قراردادها-و-معاهدات-منطقه-ای-و-بین-المللی
نام خلیج فارس در قراردادهای بین المللی
https://www.hamshahrionline.ir/xVdX
https://www.isna.ir/news/97021005937/
نام خلیج فارس در قراردادها و معاهدات منطقه ای و بین المللی
محمد عجم
https://www.magiran.com/paper/2075411
https://sanad.um.ac.ir/index.php?option=com_mag&view=htmlpage&id=628&hp=1430&lang=fa
علل تحریف خلیج فارس
عنوان نشریه : فصلنامه سیمرغ
زمینه نشریه : فرهنگی خبری، اجتماعی، علمی، ادبی
شماره نشریه : 7
تاریخ انتشار : دوشنبه, ۸ خرداد ۱۳۹۶
https://khabarban. com/18323029/
نسخه آرشیوی دریای پارس
https://www.webcitation.org/6PuCsAOso
نسخه آرشیوی دریای پارس
https://web.archive.org/web/20150310195346/http://zoodi.com/Persian-Gulf/2-naming-p-gulf.htm
https://web.archive.org/web/20140202190650/http://www.irane7000saale.com/pdf-Iran-7000/Bonyad-IranShenasi/Persian-Gulf-Hamayesh/ASNAD-NAGHSHE-TARIKHI/main-Maps-Docs-Irane7000saale.pdf
https://web.archive.org/web/20150310195346/http://zoodi.com/Persian-Gulf/2-naming-p-gulf.htm
شهر ارا : شرح چگونگی ثبت روز ملی خلیج فارس در گفتگو با محمد عجم
https://web.archive.org/web/20181015042136/http://shahraraonline.ir/final/site/news-content.php/73526?id=73526
https://web.archive.org/web/20160404121937/http://parssea.persianblog.ir/post/1/
سال 1381
https://web.archive.org/web/20140108164611/http://ajam1.persianblog.ir/
https://web.archive.org/web/20160329001026/http://parssea.persianblog.ir/1381/10/
https://web.archive.org/web/20120124012018/http://farsi-arabi.persianblog.ir/
https://web.archive.org/web/20120423231748/http://bahrefars.persianblog.ir/
https://web.archive.org/web/20160404121937/http://parssea.persianblog.ir/post/1/
کتاب خلیج فارس به زبان عربی
https://web.archive.org/web/20120511010557/http://farsi-arabi.persianblog.ir/tag/
https://web.archive.org/web/20201112214718/http://parssea.org/?m=202007
Introducing a book and Atlas
https://web.archive.org/web/20120205062033/http://www.persiangulfonline.org/asp/forum1/display.asp?messageNo=1&threadID=193
https://web.archive.org/web/20120205062023/http://www.persiangulfonline.org/takeaction/pr012805.htm
https://web.archive.org/web/20190407210545/http://parssea.org/?p=117
https://web.archive.org/web/20190331065604/http://parssea.org/?p=973
https://web.archive.org/web/20200618103154/http://parssea.org/?p=1363
کتابهای خلیج فارس شناسی
https://web.archive.org/web/20200620041041/http://parssea.org/?p=1338
دفاع حقوقی ایرانیان از نام خلیج فارس
https://web.archive.org/web/20181008115547/http://parssea.org/?p=800
روند شکل گیری و رسمیشدن روز ملی خلیج فارس:
جنگهای ایران و استعمار شوم پرتغال در خلیج فارس
https://web.archive.org/web/20160304232056/http://parssea.org/?p=4053
نویسنده : دکترمحمد عجم










No comments:
Post a Comment