A book and atlas 1
Documents on the Persian Gulf’s name the eternal heritage of ancient time”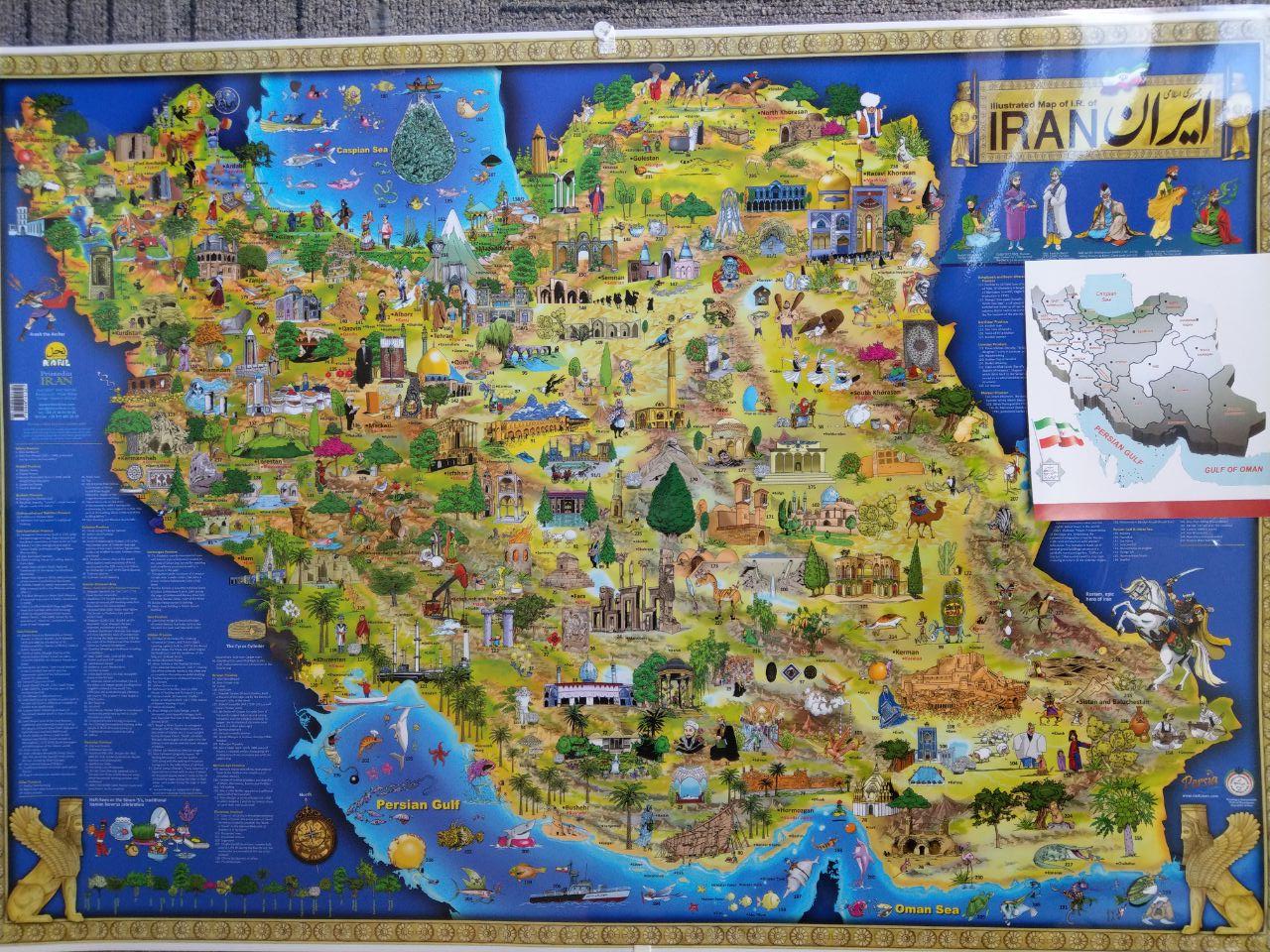
Documents on the Persian Gulf’s name the eternal heritage of ancient time”
A book and atlas part 1

Introducing the book and Atlas Persian gulf
in the picture Dr.Ali Larijani speaker of parement of Iran and some members of the parlement also deputies of MoFA Iran and india
Documents on the Persian Gulf’s name the eternal heritage of ancient time” is a book and atlas written and compiled by Dr. M. Ajam. published on 2004. A second edition was published under the supervision of
Dr. Pirouz Mojtahedzadeh and Dr.M. Ganji in 2009. The book was chosen as a candidate to receive prize of the best book of the year 2010 in Iran and was announced and ranked by the books authority of Iran among the best books in the last 50 years on the subject of ” Persian Gulf issues” in Persian language
** Awards**
At the eleventh International Festival of Iran's Best Researchs and Researchers of 2010, **this book received the Gold Coin of Excellence Award presented by the Vice President. This book has received many other awards and numerous other letters of appreciation among them a letter from former president Hashemi Rafsanjani.
This book was first published online in 2001.Then it was published in 2004 in color
And a newer version of it was released in 2009. The contents of this book have been repeatedly published in the Persian media. According to the recommendations of this book, the Persian Gulf National Day was registered by the Iranian government in 2005.
Part of the book was presented to the United Nations as a national report and published on its geographical site.
a summary of the book had been published on the UN website in 2006 under the title
A glance at the Historical, Geographical and Legal Validity of the term : Persian Gul
:It also can be read in this address
the 2006 UN report prepared by a panel of experts regarding the nomenclature is reproduced here as an Occasional Paper. Editor, MEI OP.
part of the book also had been included in the book “Persian Gulf by Javad Nourouzi and translated and published into 10 languages : Persian, Arabic, English, French, German, Italian, Spanish, Russian, Chinese and Urdu
also a famous documentary film titled Persian Gulf Name in the Course of History by Orod Atarpour has been produced and broadcasted in IRIB TV and Press TV mainly based on the document of this book.
The book has 6 chapters and some document and maps
Summary of Chapter Three of the book “Documents on the Persian Gulf’s name the eternal heritage of ancient time
What's in a name? For the Persian Gulf, quite a lot(Maps)
The book has 6 chapters and some document and maps
Summary of Chapter two and Three of the book “Documents on the Persian Gulf’s name the eternal heritage of ancient time
Nomenclature:Persian Gulf
A glance at the Historical, Geographical and Legal Validity of the term: the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf and its equivalent in different languages has been in used continuously since 2500 years ago in all languages and all over the world specially in the Arab world so that Befor 1960s not even a single case of calling “the Gulf " as the Arabian gulf been found in any text or map specially in Arabic language.
for the first time the new fake name was appeared in Arabic language in 1960s pan Arabism era.Not only ancient and past centuries texts and contracts but also all international organization and institutions also uses and recognize the term Persian Gulf as the valid and accurate term.
Below are Some Historical, Geographical and Legal reason for Validity of the Nomenclature: Persian Gulf .
1- official and unofficial maps and documents in Arabic and other languages
2- official and unofficial agreements and treaties.
3-UN and international organization and international law.
4- historical, religious and geographical books
5- Arab scholars confess for Validity of the Nomenclature: Persian Gulf .
Persian Gulf in Historical texts and Documents.
For the first time in 1971 in a UN text wrong term was used and then was corrected by a UN instruction and Note No. AD311/1GEN dated March 5, 1971.
From among the other instructions of United Nations, the following samples can be named:
- Note No. LA45.82 dated Aug. 10, 1984 (New York)
- Circular No. CAB/1/87/63 dated 16.02.1987 of Managing Director of UNESCO.
- ST/CSSER/29 dated Jan. 10, 1990.
- AD/311/1/GEN dated March 5, 1991.
- ST/CS/SER.A/29/Add.1 dated Jan. 24, 1992.
- ST/CS/SER.A/29/Add.2 dated Aug. 18, 1994.
- ST/CS/SER.A/29/Rev.1 dated May 14, 1999.
Translated and abstracted from the book:
“Documents on the Persian Gulf‘s name ancient heritage for all the time”. By : Dr.Mohammad Ajam. September 2004
The Persian Gulf and its equivalent in different languages has been in used continuously since 2500 years ago in all languages and all over the world specially in the Arab world so that Befor 1960s not even a single case of calling “the Persian Gulf ” as the Arabian gulf never been found in any text or map in Arabic language.
for the first time the new name was appeared in 1960s pan Arabism era.Not only ancient and past centuries texts and contracts but also all international organization and institutions also uses and recognize the term Persian Gulf as the valid term.
Below are Some Historical, Geographical and Legal Validity of the Nomenclature: Persian Gulf .
Introduction
The importance of the geographical names had been considered by geographers since ancient times. Through maps, atlases, and books, thePersian gulf’s name had been protected during different eras as a part of historical, cultural identity and saved as intangible heritage. For the same reason, any change, destruction, or alteration of the such unique names registered in historical deeds and maps is like the destruction of the cultural heritages. Therefore, the names of geographical features profiting from a common unique historical identity, should not be utilized as political instruments in gaining a political, tribal, and racial objective.
The Persian Gulf as the most ancient commercial naval path is located in the southwest of the Asian Continent separating Arabian plate from Iranian (Persian)
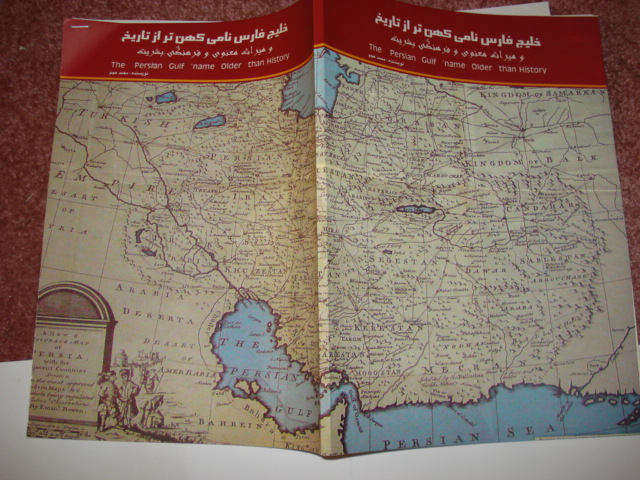
plate with a length of 1259 kilometer and a depth of average 60 m.
Name of the Persian Gulf.
Researchers and scholar, who have investigated the background of name of the Persian Gulf, became convinced of the applicability and unanimous use of the name since ancient time and at least during the past 2500 years, i.e. as of the time of the powerful Pars (Persian) Empire. has never been seen such an unanimity in the Middle East among writers and scholars on using one name during ۲ millennium history .Considering the historical background of the name Persian Gulf, Sir Arnold Wilson mentions in his book, published in 1928 that:
“No water channel has been so significant as PERSIAN GULF to the geologists, archaeologists, geographers, merchants, politicians, excursionists, and scholars whether in the past or in present. This water channel which separates the Iran Plateau from the Arabia Plate, has enjoyed an Iranian Identity since at least 2200 years ago.
also some famous Arab scholars , historian, politician and Professor as like Mohammad Aabed al Jaaberi , Abdolhadi Altazi and Abdol Moneim Saeed Ahmad al Sarraaf and … also in separate writing or interview has mentioned as:” all the maps and written deed in Arabic had referred to the bahra or khalij fars(Persian gulf)there are no single written map or document before 1960s to refer to Persian gulf as Arabian gulf and there is no need to change of a historical name.”
Background for Application wrong term
Iran and Britain signed treaties of 19 March 1809(part5)- 1812- 1814 all have mentioned Persian gulf as an Iranian sea(Britain army will not settled in any island or coast on the Persian gulf without permission of Iran(T 1809Part5- T1812P9) but Britain breached the treaties and attacked on Khark Island in 1837, the government of Iran at that time protested to England’s colonialist policy in the PERSIAN GULF and officially warned the government of Britain to avoid mischief intended at separating the Islands of the Persian gulf which is an Iranian sovereignty sea. This warning caused the Times Journal, published in London in 1840, to claim the PERSIAN GULF as
Britain Sea, but such a name never found any place.
But following nationalization of the oil industry in Iran in 1950 and dispossession of UK Companies and serving relations between Iran and UK, the Ministry of Britain Colonies, for the first time used the incorrect name of this water body.
In these years, the Arab emirates of the South of the Persian Gulf were either colonies of Britain or under its protectorate. To compensate its defeat, the representative of the UK in the PERSIAN GULF Roderick Owen published“The golden bubble on the Arabian gulf documentary”.( Publisher: London, Collins, 1957.) “ belive to be agent of MI6 Spy Org. The book was immediately translated into Arabic. In his book he suggested change of the Persian gulf name to satisfy the Arabs nationalists .
Roderick Owen wrote in the preface of his book:
“I visited PERSIAN GULF and believed that it was Persian Gulf, because I had never seen any map or deed, unless it had named the place as Persian Gulf, but by living there, I found out that the people residing at the( western) beaches are Arabs, therefore, to be polite, we should name it:Arabian Gulf.”
It is very clear that Owen was wrong. Even if he was correct it can not be a good excuse to change a historical name of an international waterway. Even now all original Arabs citizen of the 6 Arab state of GCC are less than population of Tehran. If the population or number of the countries around a sea is a criteria to change the historical name of the Persian gulf with 2500 years continuously in used then why the Indian and Pakistani shall keep the name of encircled sea around them with the current name of Arabian sea?! So Indian and Pakistani are entitled to change it to Mokran or Urdu SEA. Or African countries should change Indian Ocean. But that is not the rule or criteria the rule shall be decided by UNCSGN and UNGEGN.
In 1960, after Iran and Egypt’s disconnection of relationships and after the Arab-Israeli war, anti Iranian actions culminated due to the SHAH’s support of Israel. in a congress of Baas Party in Damascus 1970, participating heads demanded for change of the name of Persian gulfto a nationalistic , without .
relying on any legal and historical document.
The Name of Persian Gulf in Historical texts and Documents.
Few written deed has remained from before the Persian (Pars) Empire, but in the oral history and culture, the Iranians have called the southern waters ofPersiaat that time asAjamSeaand IranSeaand Pars sea.
During the years: 559 to 330 B.C. coinciding with the sovereignty of the Persian Empire over the most part of the Middle East area , especially the whole part of the Persian Gulf and some parts of the Arabian Peninsula, the name of Pars ( Persian) Sea has been widely written in the compiled texts of the different era.
In the travel account of Pythagoras, Darius sent Scylax to survey the Persian sea. several chapters are related to the description of his travels accompanied by Dariush I, to Susaand Perse polis, and the area of Persian gulf is described.
From among the writings of others in the same period, there is the inscription and engraving of Darius the Great, which belongs to the 5th century BC where, Dariush Shah , the emperor of Persian (Pars) Empire has mentioned the PERSIAN GULF Water Channel as PARS SEA, in the Hecataeus maps(472 to 509 B.C.) Persian Gulf described .
In the world map of Niark Niarjous (285-347 B.C.), Persian Gulfis described. At the same time, many maps and deeds prepared up to the 8th century by the scientists and geographical researchers such as Hecataeus, Herodotus, Hipparchus, Claudius Ptolemy, Krats Malous and in the Islamic period, also Tabari- Mohammad Ibn Mousa Khwarazmi- Abou Abu Yusef Eshaq Kindi, Ibn Khardazabeh – Batani, Masoudi (Masudi), Abou Zeyd Balkhi, Estakhri, Ibn Houghal (Ibn-e Hawqal), Aboureyhan Birouni (Biruni) and others, had explained the Persian gulf and saing that “ there is a wide sea at south of Iran named Pars Sea, (Persian), Bahre Fars, Sinus Persicus and Mare Persicum and so on.
In a book, named travels of Periplus Eritrea, the Greek ‘traveler’, of the 1st century A.D. has called the Red Sea as Arabian Gulf; the Indian ocean has been named Aritra (Eritrean) Sea; the waters at Oman Coast is called Pars Sea; Barbarus region (betweenOmanandYemencoast said to belong to Persian (Persia), and the Gulf located at south side of Iran(to the south of) is named: PERSIAN GULF. also the residence of Persians living at both sides of the Persian gulf had been confirmed .
:Islamic era
There are no any written document about Arabian coast prior to prophet Mohammad era. However, in more than 300 geographical, historical, literary, books or interpretation(Tafsir) of quran and Islamic morals, and jurisprudence, the Muslims and Arab scholars have described PERSIAN GULF from beginning day of Islamic period to the last century .from Tabari (1100 ac)to tantavee(1900) all Islamic scholar and religious leader in the different era ABAASID- FATOMID – MUGUL-
OTHEMAN – SAFAVID ERA ALL unanimously had referred to it as Persian gulf or Persian sea seperating the 2 sea
Differentiation between Persian sea and Persian gulf
The Arabian Sea historically and geographically has been referred to with different names by Turks, Persian and Arabs,expert of Geography and cartography in medieval Islam, usually named Persian sea a sea from east vak vak island (including Thailand coast and Andaman sea to the west Basra bay ) some of them called all body of water in north Indian ocean as the Persian sea (Bahre Fars) and separate it from Persian gulf (AlKhaleej AlFars ) some European geographers and travelers, also Differentiated between Persian sea and Persian gulf .
Persian Sea
Ibn al-Wardi and some of the geographers of Geography and cartography in medieval Islam were using the word Bahre Fars بحر فارس (Persian sea) to mention the current body of water in the north of Indian Ocean , Ibn Khordadbeh, Ibn Sa'id al-Maghribi, Muhammad al-Idrisi, Istakhri, Mahmud al-Kashgari, Khashkhash Ibn Saeed Ibn Aswad and Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi had mentioned the sea as Persian sea and sea of Mokran. some of the medieval map including the map by Vincenzo Maria Coronelli, 1693 had mentioned the Persian sea and also Makran. Cornelius Le Brun's Year 1718 Map.in the 16th century map by Abraham Ortelius in which the name of the Persian Sea and the Indian Sea appear.. Zakariya al-Qazwini, Al-Masudi , Ibn Hawqal, , (Hafiz-i Abru),mentioned in the book History of Islam and Iran, says:"the Green Sea is also called the Sea of India and it connects with the Persian Sea.” . Arabian Sea was first used on European maps in the colonial period . Ibn Khordadbeh, Ibn al-Faqih, Ibn Rustah, Sohrab, Ramhormozi,. Abu Ishaq Ibrahim ibn Muhammad al-Farisi al Istakhri, Abu al-Hasan Ali ibn al-Husayn ibn Ali al-Mas'udi, Al-Mutahhar ibn Tahir al-Maqdisi (d. 966), Ibn Hawqal, Al-Muqaddasi, Ibn Khaldun, Mohammad ibn Najub Bekiran, Abu Rayhan Biruni, Muhammad al-Idrisi, Yaqut al-Hamawi, Zakariya al-Qazwini, Abu'l-Fida, Al-Dimashqi, Hamdollah Mostowfi, Al-Nuwayri, Ibn Batutta,Katip Çelebi and other sources have used the terms, "Bahr-i Mohit i Ajam", "Bahr-al-'Ajami", "Bahr-i-Fars", "Dera-i-Fars"(Persian), and "Bahr-i Mokran/Mecran", "Bahr-i Al Akhzar" (green) to refer to the current Arabian sea. ("Bahr-in Arabic means Sea" and Mohit means ocean) none of them had referred to as Arabian Sea.
In the Book Documents on the Persian Gulf's name( https://kids.kiddle.co/Documents_on_the_Persian_Gulf%27s_name )
Pages 60 to 84 are devoted to the description of the Persian Sea in the books of geographers and historians of Muslim world
All of whom had called the seas of south part of Iran , india and the Arabian Peninsula as the Persian Sea, the book cited description of the Persian sea from the book (Sourat Ard)Face of the Earth page 42 Written by Ibn Hawql: ” … after Arabs lands then should be mentioned The Sea of Persia because Persian sea includes most of Arabs borders, and the Arab peninsula are connected to this sea ,the Persian sea connected to many countries of Islam. this sea start from the Qulzam(Red sea ) it ends to Eble (Basra bay), then It crosses Siraf (Bushehr) then extends to the coasts of Hormuz then Makran and the coasts of Multan, which is the coasts of Sindh (Pakistan) which the boundary of the country of Islam has ended then the persian sea continues to the coasts of India then connect to to the sea of China”. see original text: https://al-maktaba.org/book/11780/47
Persian Sea, the old name of the vast sea covering the all southern seas of Iran and many other part of the Asia . Muslim geographers referred to a wide body of water as the Persian sea,they were considering the world only have 7 seas and the vast sea is persian sea and Rum sea.
some other scholar of medieval Islam who mentioned persian sea are :
In 290 (Islamic calender.H ) Ibn Rasta, separated the Persian Gulf from vast sea of Persian sea for the first time, (book Al-A'laq al-Nafisa, p. 84);
in 266 (Islamic calender.H ), Qadama Ibn Ja'far called it the Persian Sea (p. 233).
in 290 I.C.H , Sohrab (Ibn Sarabiun) called it the Persian Sea and the sea of the Persia (pp. 59,78);
in 332 (Islamic calender.H ) Masoudi (edition 1967, p. 38, vol. 1, p. 128) has explained it as the Persian Gulf branch of the Persian Sea.
In 340 Istakhri (1967, p. 28), and in 342 Bozorg Ibn Shahriyar Ramhormozi (p. 41) and in 375 Mohammad Ibn Ahmad Moghaddasi (pp. 17-18) called it the Persian Sea and in 355 Motahar Ibn Tahir Moghaddasi (vol. 4, p. 58) said the Persian Gulf a branch of the Persian sea
in 367 Ibn Hawql (p. 42) the Persian Gulf and the Persian sea
in 372 Sahib Hudood al-Alam (p. 12) it is the Persian sea
in 420 Abu Rihan al-Biruni (p. 167) the Persian Sea and the Persian Gulf.
In the book Masalak al-Mamalak, the Persian translation of the fifth / sixth century AH the Persian Sea is the great sea, (Istakhri, 1989, p. 109).
In 500 AH the book of Ibn Balkhi it described the Persian Sea (p. 153)
in 605 Muhammad ibn Najib Bakran called it the Persian sea (p. 18,20)
in 625 the Yagout described the Persian Sea (vol. 1, p. 502),
in the eighth century Hamdollah Mostofi Persian sea from Sindh to Oman has been recorded as part of the Persian Sea (p. 136).
In the third century, Ibn Faqih connected the Persian Sea to the Indian Sea and considered both as one sea (p. 8).
According to Ibn Rasta, the Persian Gulf branched off from the Indian Sea (p. 84).
Istakhri considered the extent of the Persian Gulf as far as India (edition 1967, pp. 28-29) and in the book Hudood al-Alam as its limit up to the Indus (p. 12).
According to Ibn Balkhi, the Persian Sea was connected to the Red Sea (ibid.)
Idrisi wrote the green sea is the Persian Sea and blived it is connected to the China Sea (Vol. 1, p. 9). Yaghoot also considers the Persian Gulf as a branch of the Great Indian Sea . http://lib.eshia.ir/23019/1/577 This shows that in colonial times, the Arabian sea was not used by arabs and muslems scholars .
In Turkish language Arabian sea was called as Oman sea or Persian sea , this name was used by most of the ottoman geographer such as Piri Reis and others among them Kâtip Çelebi in the "Tuḥfat al-kibār fī asfār al-Bihār" ('A Gift to the Great concerning Naval Expeditions') (1656) –The History of the Maritime Wars of the Turks (1831) English translation by James Mitchell. referred as Oman sea and also Persian sea and some other Ottoman Empire maps were using Bahre Ajam (Persian sea)such as in Cihannümâ (Katip Çelebi)
https://www.nytimes.com/2016/01/13/world/middleeast/persian-gulf-arabian-gulf-iran-saudi-arabia.html ...Persian Gulf Is Caught in the Middle of Regional Rivalries .
^"The Voyage around the Erythraean Sea". depts.washington.edu.
- ^"Archived copy". ^Mitchell 1831.
- ^“A Jewel of Ottoman Naval History: The Book of Kâtip Çelebi on Naval Campaigns" in the MuslimHeritage.com
- ^"Ottoman Maritime Arsenals And Shipbuilding Technology In The 16th And 17th Centuries" Archived 2013-10-14 at the Wayback Machine in the MuslimHeritage.com
- ^http://www.persiangulfstudies.com/fa/pages/875/دریای-مکران-یا دریای عرب
- ^"persian sea bahre fars: Author: group of Writers". http://wikifeqh.ir.
- ^"Al-Massalek wa al-Mamalek", Leiden edition, 1889. p. 233
- ^The abrdiged "Al-Buldan", Leiden, 1885, p. 8
- ^Ibn Rustah, Kitāb al-A'lāk an-Nafīsa, ed. M. J. De Goeje, Bibliotheca Geographorum Arabicorum [BGA], Leiden, E. J. Brill, 1891/1892. p. 81
- ^Ajayeb al-Aqalim al-Saba ila Nehayate al-Mara, (Vienne: 1929), p. 59. 9th century AD.
- ^Nakhoda Bozorg ibn Shahriyar Ramhormozi was another Persian geographer of the classical Islamic era, "Ajayeb al-Hind", ed: M. Davis, Leiden 1886, p. 41
- ^"Massalek al-Mamalek", ed.: De M.J. Goeje, Leiden 1927, p. 28
- ^"Muruj adh-dhahab wa ma'adin al-jawhar (The Meadows of Gold and Mines of Gems)", English Translation by Aloys Sprenger, Vol I, (London: 1841), p. 259
- ^al-Bad’ wa-l Tarikh, (Paris: 1907) Tom IV, p. 58.
- ^"The Oriental Geography of Ebn Hawkal", Translated by Sir Williams Ouseley (London: 1800) p. 62; "Surat al-Arḍ"(Leiden 1938), Vol I, p. 42.
- ^Ahsan al-Taqasim fi Ma’rifat al-Aqalim. Ed: De A.J. Goeje, (Leiden 1906), p. 17.
- ^"Jahan Nama", Vol I. p. 44. .
- ^"Al-Tafhim le-awa’el Sena al-Tanjim" ed.: Jalal al-Din Homai (Tehran: 1318 Hijri Sola Calendar), p. 167. Also in "Qanun Masudi"(Heydarabad, 1955), Vol. II. p. 558.
- ^"Geographic d’Edirisi" traduite de l’Arabe en Francais par P. Amedee Jaulert (Recueil des voyages et des memoires publiees par la Societe de Geographie), (Paris: 1840), Vols. VI and VI. "Nuzhat al-Mushtaq fi Ikhtraq al-Afar", (Rome : 1878). p. 9
- ^"mu’jam al-Buldan",(Cairo: 1906), Vol. 2, p. 68.
- ^"Athar al-Bilad" (Gutingen: 1848), p. 104.
- ^"Taqwim al-Buldan", Geographie d’Aboulfeda traduite de l’Arab par M. Reinaud, 2 Vols. (Paris: 1848), Vol 1, p. 23.
- ^"The Travels of Ibn Babutta", translated from the abrdiged Arabic MMS of Cambridge by the Rev. Samuel Lee(Cambridgde: 1824), p. 56
- ^http://www.persiangulfstudies.com/fa/pages/875/دریای-مکران-یادریای عرب
«بحر فارس» و «خلیج فارس» فی المعاجم اللغویة والمصادر الأدبیة
عجائب بحر الهند و فارس و جزائره
https://sonsofsunnah. com/2015/09/11/النبی-العربی-سمى-الخلیج-بحر-فارس/
("Bahr-in Arabic means Sea" and Mohit means ocean) none of them had referred to as Arabian Sea.
an official map of the Otheman saltanat
Hegemony of Portuguese in the Persian gulf
In 1507 A.D.Portugal’s navy captured Hormuz Island under commandment of Alphonso Burkerk and it continued till 1620. In a research essay, Dr. José Manuel Garcia, professor and a member of Geographical Society
of Portugal emphasized the name of Persian Gulf in the official and unofficial deeds and maps of Portugal since 1507 so far. The maps prepared by the Portuguese on Persian Gulf are kept in museums as mankind heritage.
From among 50 maps and letters exchanged during the years: 1500 to 1700
A.D. among the governors of Persian Gulf and the kings of Portugal and Spain or those mentioned in books and writings of tourists,Persian Gulf has been named as follows:
Mare de Persia, Persico Sinus, mare Persio, Mare Persicum, Mar Persiano, Persiski Zaliv, Persischer Golf,ParsSea, Bahre Fars, Perza obol, Persiste Habbugt.
Persian Gulf in Arabs Contracts and Accords
As of 1800 to 1970, at least in 45 contracts concluded among the tribal leader(Emirates) or countries such as Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Ottoman, Oman, Emirs of Motesalehe (United Emirates), compiled in English and Arabic, the name of Persian Gulf(bahre fars) has been used.
In a book published in UAE 1989 by Rashed Ali Mohammad titled : (Economic and political agreement between the Arabs Emirs and Britain 1806-1971) he had included original of around 22 contracts in all of them in both Arabic and English text the name of Persian gulf had been mentioned.[1]
:From among the aforesaid contracts the following can be mentioned:
۱٫ General contract with Arabian Emirs on Jan. 8, 1820 between Sheikhs of United Emirates atPersian Gulf, signed by General Cair and 11 chiefs of Arab Tribes, the word: Al khaleej Al Farsi has been used in the Arabic texts.-
۲٫ Treaty of 1856 and ۱۹۴۷ on Prohibition of Slaves trades.-
۳٫ Permanent Contract of Peace in 1853.-
Contract on Independence of Kuwait (this deed was registered on June 19, 1961 with Secretariat of United Nations.
Treaty on Determination of Border Lines ofIraqandKuwait(1996)-
Even Nasser the pan Arabic leader of Egypthad used the term of (al khaleej al Farsi) Persian gulf in all his speeches and his books and articles before war 1967.
Persian Gulf in all Historical Maps of the region
In all the important historical maps and Atlas whether modern or belonging to previous centuries, the water artery located at south ofIranhas been registered asPersian Gulf. In the Arabian countries too, it has always been namedPersian Gulfup to the 70s. For instance, in the Atlas “Al araq fi Al khavaret Al ghadimeh” by Dr. Ahmad Souseh (Baghdad 1959) including 40 maps among the Arabian sources of the Middle Ages all have the Arabic term for the Persian gulf.
In the maps presented by Arabian countries to the International Court of the justice for settlements of border claims, the name ofPERSIAN GULFhas been mentioned in their documents.
– Atlas of La Péninsule Arabique dans les cartes Européennes Anciennes (The Arabian Peninsula in Old European Maps).Paris, Monde Arabs institute and Tunisia university IMA & Khaled. Al Ankary, 2001. ۴۲۴pp. contains ۲۶۰ maps with details about each map in 3 languages: Arabic, English and French. Almost all of these 260 maps have the correct name of Persian Gulf.
Moreover, 10 maps have used both Persian Gulf for the gulf and also persian Sea (for the current area of Seaof Oman and Arabian sea) •
The book: Roots of Kuwait. “Osoul Alkuwait Almanshour Alalam” (1991) published in theNetherlandsalso contains 15 maps where the name of PERSIAN GULFexists.
- In the “Atlas of Alkuwaitfi Al kharaet Al Aalam” some maps have been used where there exists the name ofPERSIAN GULF.
In Atlas of “Alkuwaitfi Al kharaet Al tarikhieh” published by the efforts of Abdollah Yousef Al ghanim in 1994, there are about 200 maps mentioning the name ofPersian Gulf
- In the ARABIC book: “Al khalij al fars Abar Al tarikh va Al ghoroun” (written by Mohammad Mirza, 1976Cairo) there are 52 maps drawn out of Arabic sources, all have the name ofPersian Gulf.
- In Atlas of “History of Islam” (1951-55AmericaandEgypt) the namePersian Gulf has been mentioned IN ۱۶
- In the Atlas of “Khalij (Gulf) in the Historical Maps” published in UAE (۱۹۹۹) more than 600 maps have the term Persian gulf.
- The Arabic Bank and Beyt Al quran inBahrainpublished a large wall calendar in 1996 containing the 11 historical map ofBahrainin which all the maps contain the

.jpg)
- name of Persian Gulf
It is interesting that from among 6000 existing historical maps published up to 1890, there are only three maps mentioning the names of Basreh Gulf, Ghatif Gulf, and Arabic Gulf, this name in fact are the name of bays of the Persian gulf. in local language they call the bay also as the gulf like :gulf of Busher-ChahBahar Gulf,SirafGulf,BasrehGulf,Ghatif Gulf,Bahrain Gulf, Basre gulf …. but such names are not applied to the entirety of the Persian Gulf.
It is obvious that the promotional use by the Arabs of the three aforementioned maps, whose identity and originality are not clear, in comparison with 6000 maps and more than 300 historical and credible geographical books from ancient time to 20thcentury , shall lack any value.
In the Arabic Dictionaries like Al Monjed, and also in all (60)Qoranic Tafsires and religious Islamic books and in all treaties ( more than 30 Arabic treaties between the Arabs tribe leader with theUKand Othman and Iranians )Persian gulfhas been used .
In the many museums all over the world some can find maps or manuscript having the name Persian gulf some recorded as intangible world heritage (UNESCO) In Library of American Congress, Britain National Library (London), deeds at Ministry of India’s Affairs (London), Library of Faculty of Orientals Studies of London, there are more than 300 maps, containing the name Persian Gulf. In Eskandria Library of Egypt And National Musum Of Egypt alsoPersian gulfmap are preserved.
Furthermore, about 30 valid Atlas have registered the name ofPERSIAN GULFwithin the past 300 years, such as: Atlas of Thomas Herbert (1628).
– Atlas of Pars,LousajUniversity(1863). – Atlas ofGermany(1861), Pars Envile Atlas (1760).- Atlas of Modern Geography (1890).- Atlas of London (1873),- Atlas of Ernest Embrosius (1922),- Atlas of Bilefild (1899)- Atlas of Harmsorth (19th Century, London). – ….
In 18th to 20th centuries when theUKexpanded its dominance over the seas and appeared as protectorate of the Sheikhs on the south sectors of the PERSIAN GULF, the official maps and documents of the areas in all languages refers to the GULF asPERSIAN GULF.
Applications of the Name Persian Gulf by International Organizations
Not only the Persian Gulf had been used since ancient time in all languages but also in current time non Arabs countries had never recognized a new tribal name and UN and all international Organizations and affiliated foundations have applied the correct name of PERSIAN GULF.
** Some of the most important historical atlases of the persian gulf are as
..:.. نقشهها 100Maps animation 100 .)
درگذر زمان نامه های تاریخی نیز
The earliest known world maps date to classical antiquity, the oldest examples of the 6th to 5th centuries BCE still based on the flat Earth paradigm. World maps assuming a spherical Earth first appear in the Hellenistic period. The developments of Greek geography during this time, notably by Eratosthenes and Posidonius culminated in the Roman era, with Ptolemy's world map (2nd century CE), which would remain authoritative throughout the Middle Ages.
With the Age of Discovery, during the 15th to 18th centuries, world maps became increasingly accurate; exploration of Antarctica, Australia, and the interior of Africa by western mapmakers was left to the 19th and early 20th century.
In all maps, documents and correspondence until 1960, the name of the Persian Gulf and its equivalents were used for body of water between Iran and Arabia.
According to the book “Documents on the Persian Gulf's name”by Dr.Ajam .
A number of these maps and documents are introduced and published in the following Atlases:
* Atlas "“The Gulf in Historical Maps” 1478 1861-,Leicester, 1996. 2th edition in 1999 , Alqasimi, Sultan bin Mohammad, 70 maps Of the Persian Gulf
** Atlas of geographical maps and historical documents about the Persian Gulf from prehistoric times to the present Published by Sahab Institute of Geography and Cartography in 1971 in Tehran.This atlas consists of eight chapters, and 80 maps. The maps collected in this atlas are the work of great geographers and historians of Iranian, Arab, European, Indian, Roman, Egyptian, central Asia, African and American.
***" Atlas of "Description of the Persian Gulf in Historical Maps" was published in 2008 by the Iranology Foundation, in Iran which presents 40 maps of the Islamic Middle East cartographer and 120 European
@@ Maps of colonial era***
- Atlas of The Arabian Peninsula in Old European Maps (253 maps) by Khaled Al Ankary, Institute du Monde Arabe,ParisandTunisiaUniversity,2001. all 253 maps of this atlas has been printed in color and in 3 languages and named the Persian gulf and also the maps in pages:-141-226-323-322-331-345-347-363-355 have mentioned persian gulf for the Gulf and also persian sea for the body of water of current Arabian sea and Gulf of Oman , such as the famous hours shape map of Bunting H.S.Q34/24CM Hanover,1620.
- List of some early maps which had mentioned the Persian Gulf and also some famous atlases explained the Persian Gulf:
- Map of Babylonianmaps. Babylonian Map of the World. the oldest known world map, 6th century BCE Now in the British Museum.
- Map of Anaximander world map-Reconstruction of Anaximander's map
- Map of Hecataeus world map- Reconstruction of Hecataeus' map
- Map of Mappa di Eratostene.1883 reconstruction of Eratosthenes
- Map of World map hedo.A 1628 reconstruction of Posidonius ideas about the positions of continents (many details couldn't have been known by Posidonius)
- Map of Map Pomponius Mela rotated.An 1898 reconstruction of Pomponius Mela's view of the World.
- Map of Ptolemy-World Vat Urb 82.The oldest surviving Ptolemy's world map Ptolemaic world map, redrawn according to his 1st projection by Orthodox monasticismmonks at Constantinople under Maximus Planudes around 1300
- Map of Ptolemy World Map.Nicolaus Germanus's 1467 Latin world map according to Ptolemy's 2nd projection, the first known to the west
- Map of World Map by Cosmas Indicopleustes.
- Map of Ibn Howqal World map. by Ibn Hawqal (south at top)
- Map of Cotton world map.The Anglo-Saxon 'Cotton' world map (c. 1040).
- Map of Beatus map.World map from the Saint-Sever Beatus
- Map of Kashgari , Mahmud al-Kashgarial-Kashgari's ''Diwanu Lughat at-Turk''.
- Map of Tabula Rogeriana upside-down. (1154).
- Map of Hereford Mappa Mundi 1300.The Hereford Mappa Mundi.
- World map pietro vesconte. Pietro Vesconte's world map, 1321
- Map of Catalan-Atlas - Two leaves of The world atlas
- Map of Da-ming-hun-yi-tu.Da Ming Hunyi Tu map
- Map of KangnidoMap.Kangnido world map (1402)
- Map of DeVirgaDetail.De Virga world map (1411–1415)
- Map of Biancomap.Bianco world map (1436)
- Map of Mapa_de_Borgia_XV.Borgia map (early 15th century)
- Map of Genoese map.Genoese map of 1457, Biblioteca Nazionale at Florence
- Map of FraMauroDetailedMapInverted.Fra Mauro map (1459)
- Map of Martellus world map.Martellus world map (1490)
- Map of Behaims Erdapfel.Behaim's Erdapfel
- Map of Juan de la Cosa-North up.Map of Juan de la Cosa, shown rotated right (in the original manuscript north points left), 1500
- Map of Cantino planisphere 1502, Biblioteca Estense, Modena
- Map of Caverio Map circa 1506, Bibliothèque Nationale de France, Paris
- Map of Ruysch map.Johannes RuyschRuysch's 1507 map of the world
- Map of Waldseemuller map 2.Waldseemüller map with joint sheets, 1507
- Map of Piri reis world map 01.Fragment of the Piri Reis map by Piri Reis in 1513
- Map of Piri reis world map 01.Piri reis world map 01
- Map of PietroCoppo.Map of Pietro Coppo, Venice, 1520
- Map of Map Diego Ribero 1529.World Map by Diogo Ribeiro, "Propaganda map" (1529), Biblioteca Apostolica Vaticana
- Map of Mercator 1569.pngGerardus MercatorMercator ''Nova et Aucta Orbis Terrae Descriptio'', 1569.
- Map of Abraham OrteliusOrtelius' world ''Theatrum Orbis Terrarum'' (1570)
- Map of 1581 Bunting clover leaf map.''Die ganze Welt in einem Kleberblat'' (The entire World in a Cloverleaf). Jerusalem is in the centre of the map surrounded by the three continents.
- Map of Kunyu Wanguo Quantu (坤輿萬國全圖). (1602), Japanese copy
- Map of Nova totius Terrarum Orbis geographica ac hydrographica tabula (Hendrik Hondius) balanced. IIHendrik Hondius, ''Nova Totius Terrarum Orbis Geographica ac Hydrographica Tabula'', 1630
- Map of Orbis Terrarum Nova et Accuratissima Tabula by Nicolaes Visscher, 1658.
- Map of 1794 Samuel Dunn Wall Map of the World in Hemispheres - Geographicus World2-dunn-1794. (mathematician)
- World Map 1689. Van Schagen's map of the world, 1689
- Map of persia. Persian Gulf 1747 Boen.
- Persian(IRAN) Empire 1747. karta Persian Gulf1747
- Saudi King letter.Saudi King letter PERSIAN GULF
- ALKHALEEJ ALFARSI 1952.Saudi map of Persian Gulf
- Map of Iraq in Iraqi carpet 1970. Persian Gulf Iraqi carpet 1970.
- Basra bahrefars.turkey: BahreFars( Persian Gulf)
- Cairo street..A street in Cairo named Persian Gulf 1958
- Heinrich Kiepert. Imperia Persarum et Macedonum. 1903. Persian Gulf.
- Soulier, E.; Andriveau-Goujon, J. Anciens Empires Jusqua Alexandre. 1838.
- Map Pomponius Mela rotated.An 43 AD.Karata Persian Gulf
- Ptolemy Cosmographia 1467 - Arabian peninsula. Persian Gulf .
- Mappa di Eratostene. 194 BC Eratosthenes karta Persian Gulf
- Istakhri map 2.Regional - Persian Gulf Istakhri,1200
- Ottoman Asia (partial, 1893).1893 Karata Persian Gulf (Ajam)
- Saudi map of Persian Gulf 1952. الخلیج الفارسی.
- Map of Persial Gulf- Amsterdam-1640.Karata Persian Gulf 1640
- Map of the region bounded by the Saudi Peninsula, Red Sea. Jacob van Merus, 1680,Karata Persian Gulf Amesterdam
- Regno di Persia con le notitie delle ... Publication Date 1679 Scarce map extending from the Eufrate to the Indo.Showing major rivers, mountains and cities. From Il Mercurio, by De Rossi. 1679 .
- Perse Turquie Asiatique et Arabie old map Desnos 1766. Persian Gulf
- Antique map La Perse Bellin 1764.Karata Persian Gulf 1764'''
- Persia Sive Sophorum regnum Old map Persia Merian 1638.
- Jansson's map of Persia..Amsterdam karta Persian Gulf1640
- Map of Asia in the shape of the mythical winged horse Pegasus.. 1581 Hannover Karata Persian Gulf
- 1732 Asia issued.. 1732 Guillaume Danet. Persian Gulf
- Map of Amsterdam1685.. Karata Persian Gulf 1700
- Detailed map of Asia..Nuremberg / 1744 karta Persian Gulf
- Important Jodocus Hondius.... Amsterdam 1620 karta Persian Gulf
- Published in Amsterdam.png by Nicholas Visscher the Elder.1670.
- Map of K. Johnston -1850-Edinburg.A.K. Johnston -1850-Edinburg
- Map of George Rollos 1770 London.
- Map of Guillaume de L'Isle - 1731- Paris.
- Map of J. Rapkin , Published by Tallis.-1851-london.1851-
- Location of and gulf by Janssonius, Joannes- 1640-Amsterdam.
- Map of Mercator, Belgium, 1578.Mercator, Belgium, 1578
- Map of Published by D'Apres de Mannevillette-1775-paris .
- Map of Robert- 1760- Paris. 1760- Paris .
- Map of The London Geographical Institute 1890, Published by George Philip & Son. 1890, Persian Gulf
- Map of V. Levasseur - Paris- 1838.V. Levasseur -
- Amsterdam J. Covens et C. Mortier,1720.Amsterdam 1720 Persian Gulf
- Strassbourg 1525 by Lorenz (Laurent) Fries.Strasbourg 1525 karta Persian Gulf
- Rigobert Bonne- 1771 Paris.Rigobert Bonne- 1771 Paris.
- Map of Nova Orbis Tabula In Lucem Edita, A.F.de Wit.. Amsterdam-1680 ca Karata Persian Gulf
- Map of Typus Orbis A Ptol. Descriptus.-1542
- Map of Die beyden Halbkugeln.'''Die beyden Halbkugeln-Vienna-1790'''
- Mappemonde a l'usage du Roy Par Guillaume Delisle Premier. 1720 (Shows De Gama Land)
- Mappe Monde Carte Universelle de la Terre Dressee Sur les Relations les plus nouvelles.Karata Persian Gulf -1755'''
- Persia, Caspian Sea, done by ye Czar, and Part of Independent Tartary. 2700 Persian Gulf
- Middle East Antique map Babylon Assyriens Philippe 1787. Persian Gulf
- Map of Persia Kingdom Ormus Strait Hormuz Old plan Bellin 1756.
- Japanese Map of Saudi Arabia.Japanese karta Persian Gulf1874
- Brodersen, Kai. 2012. "Cartography." In ''Geography in Classical Antiquity.'' By Daniela Dueck, 99–110. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ. Press.
- Edson, Evelyn. 1993. "The Oldest World Maps: Classical Sources of Three Eighth Century Mappaemundi." ''Ancient World'' 24.2: 169-184.
- Fox, Michael, and Stephen R Reimer. 2008. ''Mappae Mundi: Representing the World and Its Inhabitants In Texts, Maps, and Images In Medieval and Early Modern Europe.'' Edmonton, Alberta: Department of English and Film Studies, University of Alberta.
- Goffart, Walter. 2003. ''Historical Atlases: The First Three Hundred Years,
1570–1870.'' Chicago: Univ. of Chicago Press.
- Harwood, Jeremy, and A. Sarah Bendall. 2006. ''To the Ends of the Earth: 100 Maps That Changed the World.'' Cincinnati, OH: David & Charles.
- Harvey, Paul D. A., ed. 2006. ''The Hereford World Map: Medieval World Maps and their Context.'' London: British Library.
- Shirley, Rodney W. 1983. ''The Mapping of the World: Early Printed World Maps 1472-1700.'' London: Holland Press.
- Talbert, Richard J. A., ed. 2000. ''Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World.'' Princeton, NJ: Princeton Univ. Press.
- Wendt, Henry, John Delaney, and Alex Bowles. 2010. ''Envisioning the World: The First Printed Maps 1472–1700.'' Santa Rosa, CA: Sonoma County Museum.
- Woodward, David. 1985. "Reality, Symbolism, Time, and Space in Medieval World Maps." ''Annals of the Association of American Geographers'' 75.4: 510-21.
- For more maps in the PART 2 : https://japan.mfa.gov.ir/en/newsview/536033
 :
:
- ۱- Atlas of The Arabian Peninsula in Old European Maps (253 maps) by Khaled Al Ankary, Institute du Monde Arabe,ParisandTunisiaUniversity,2001
all 253 maps of this atlas has been printed in color and 3 languages and have the corect name of Persian gulf also the maps in pages:
-141-226-323-322-331-345-347-363-355 have mentioned persian gulf for the Gulf and also persian sea for the body of water of current Arabian sea and Oman gulf , such as the hours shape map of Bunting H.S.Q34/24CM Hanover,1620.
۲- Atlas of Historical maps of the gulf by sultan muhammad al qasimi Sharjeh 500 maps of the persian gulf .
- ۳- Atlas ofIraqin old maps. by Ahmad Sussa 39 old maps of arabic and islamic sources all have the correct name of persian gulf(Bahre Fars)
- ۴-Kuwaitin the maps of the world 1992 . contan 80 maps all have the Persian gulf name.
- ۵-Kuwait reading the historical maps, 200 maps ,1994 .
- ۶-Roots of Kuwait, 15 maps ,1991.
- ۷-description of the Persian gulf in the historical maps by Iranology foundation, 40 maps of Islamic scholars and 120 maps of European famous cartographers 0f 1500-1900 AD.by Dr Hassan Habibi 2007.
Tehran.all the maps have the name Persian gulf. and many other atlases have also been published and they have been described in the book: Documents on the Persian Gulf’s name .[14]
International Organizations
International organization and Intergovernmental organization uses the Persian gulf as the international recognized term.
Written description by Muslim travelers and European geographers . Among historians, travellers and geographers of the Islamic era, many of them writing in Arabic or persian from the 9th to the 17th century, Ibn Khordadbeh, Ibn al-Faqih, Ibn Rustah,[5] Sohrab, Ramhormozi, Abu Ishaq Ibrahim ibn Muhammad al-Farisi al Istakhri,[8] Abu al-Hasan Ali ibn al-Husayn ibn Ali al-Mas’ud, Al-Mutahhar ibn Tahir al-Maqdisi (d. 966), Ibn Hawqal, Al-Muqaddasi, Ibn Khaldun, Mohammad ibn Najub Bekiran, Abu Rayhan Biruni,[14] Muhammad al-Idrisi, Yaqut al-Hamawi, Zakariya al-Qazwini,,Abu’l-Fida, Al-Dimashqi, Hamdollah Mostowfi, Al-Nuwayri,[19] Ibn Batutta, Katip Çelebi and other sources have described the Persian gulf and used the terms, “Bahr-i Fars”, “Bahr-i Ajam“, “Bahr-i-Farsi”, “Dera-i-Fars”(all refers to Persia) and are equable to Persian gulf or Persian sea .
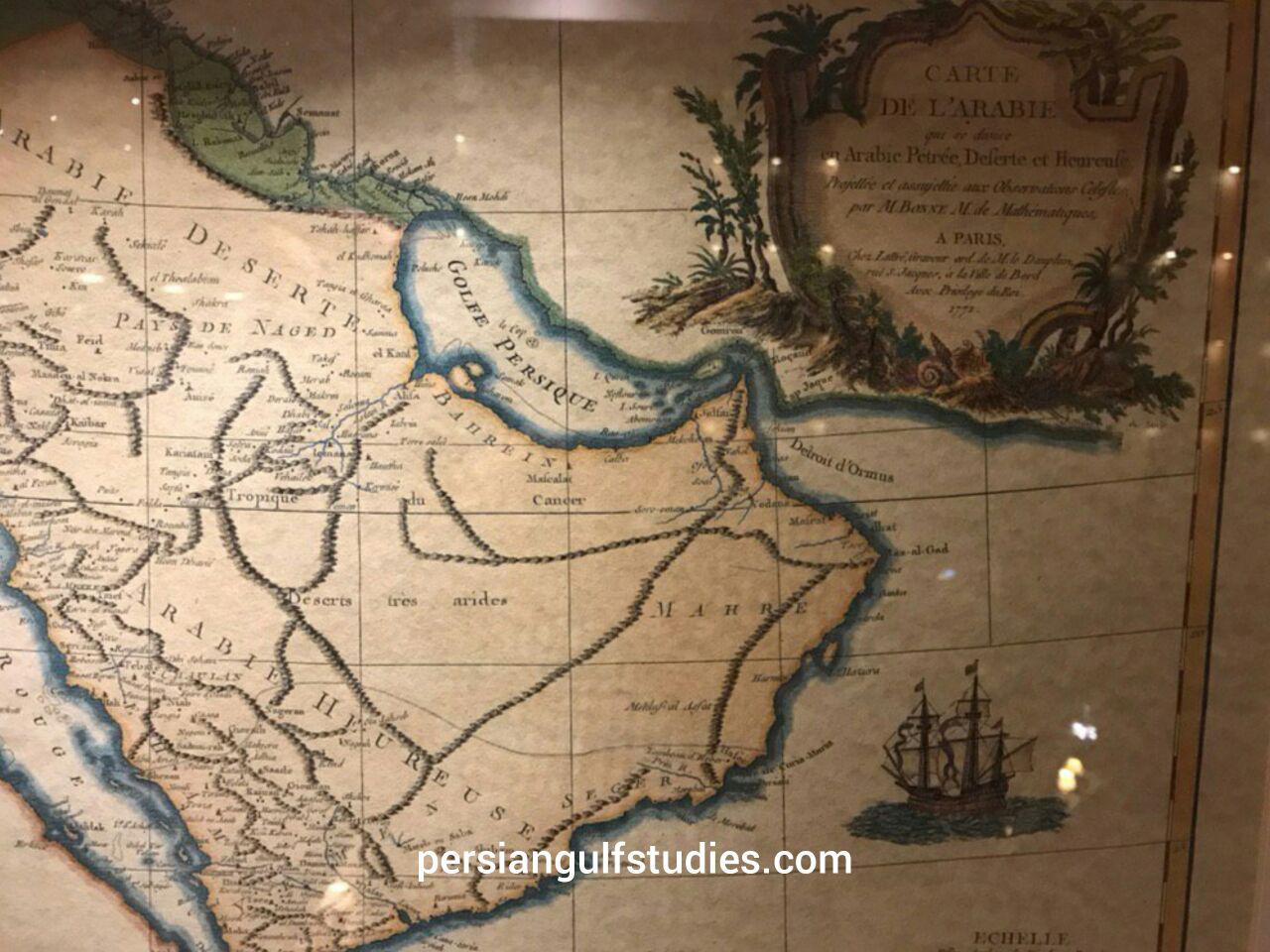
Iranian has always respected the geographical names such as for the Arabian sea although for the Arabian sea and the gulf of Oman historically other names had been used such as Mokran sea- Persian sea- Akhzar sea … some arab scholar had wrote to justify the change of the term Persian gulf they claimed that Arabian gulf also had been used in ancient time they had mentioned pliny book . but infact pliny had never mentioned Persian gulf as Arabian gulf :below is the PLINY text BOOK:
Pliny: Natural History ۶٫۹۶-۱۱۱٫ (On India)
XXVIII107. Moreover in this region the sea then makes a double inroad, into the land; the name given to it by our countrymen is the Red Sea, while the Greeks call it Erythrum, from King Brythras, or, according to others, in the belief that the water is given a red colour by the reflexion of the sun, while others say that the name comes from the sand and the soil, and others that it is due to the actual water being naturally of such a character. [108] However, this sea is divided into two bays. The one to the east is called the Persian Gulf, and according to the report of Eratosthenes measures 2500 miles round. Opposite is Arabia, with a coastline 1500 miles in length, and on its other side Arabia is encompassed by the second bay, named the Arabian Gulf; the ocean flowing into this is called the Azanian Sea. The width of the Persian Gulf at its entrance some make five and others four miles ; the distance in a straight line from the entrance to the innermost part of the Gulf has been ascertained to be nearly 1125 miles, and its outline has been found to be in the likeness of a human head. [109] Onesicritus and Nearchus write that from the river Indus to the Persian Gulf and from there to Babylon by the marshes’of the Euphrates is a voyage of 1700 miles.
: Translated and abstracted from the book:
Documents on the Persian Gulf‘s name: : the eternal heritage of
ancient time By : Mohammad Ajam
اسامی جغرافیایی باستانی میراث بشریت،
و در کتاب دومین همایش ژئوماتیک 1382سازمان نقشه برداری نیز منتشر شده است
در صورتی که می خواهید در اثر پژوهشی خود به این مقاله ارجاع دهید، باید از عبارت زیر در بخش منابع و مراجع استفاده نمایید: عجم, محمد، ۱۳۸۲، اسامی جغرافیایی باستانی میراث بشریت،
پژوهشی در مورد دو نام خلیج فارس و خزر و چالشهای فرا روی، همایش ژئوماتیک 82، تهران، سازمان نقشه برداری کشور، https://www.civilica.com/Paper-GEO82-GEO82_74.html
دیباچه مقاله:
(انیمشن نقشهها :Maps animation....)
درگذر زمان نامه های تاریخی نیز همانند انسانها دستخوش حوادث و رویدادهای اعم از سیاسی، اجتماعی و یا فرهنگی بوده اند
مصون مانده است.
Also : http://persiangulfstudies.com/fa/index.asp?p=pages&ID=781&Sub=779
- ^IRIB
- ^United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names Working Paper No. 61, 23rd Session,Vienna, 28 March – ۴ April 2006. accessed October 9, 2010
- documentary on the persian gulf history[3]
- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gicoXMuqP_w&feature=player_embedded
- a historical documentary on the name ofPersian gulf
- documentary on persian gulf
[[۴]]
- Documents on thePersian Gulf’s name : the eternal heritage of ancient time
Author: Ajam, Muḥammad. [۵] [۶] و documentary on the name Persian gulf .
[۱] ^ the book was introduced in Asia Times -2012 . Asia’s most trusted news source for the Middle East
- ^Bosworth, C. Edmund. “The Nomenclature of the Persian Gulf.” Pages xvii-xxxvi in Alvin J. Cottrell (ed.), The Persian Gulf States: A General Survey. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1980.) (pg xxxiii).. Excerpt: Not until the early 1960s does a major new development occur with the adoption by the Arab states bordering on the Gulf of the expression al-Khalij al-Arabi as weapon in the psychological war with Iran for political influence in the Gulf; but the story of these events belongs to a subsequent chapter on modern political and diplomatic history of the Gulf.
- ^Agapius on a boat, retrieved 24 Feb. 2009.
- ^ALAI, CYRUS. “GEOGRAPHY iv. Cartography of Persia”. Encyclopædia Iranica. Retrieved 2012-02-01.:
After World War II, some circles decided to change the name of the Persian Gulf to Arabian Gulf. Although the government of Persia opposed the move vehemently, in some editions of a few maps and atlases the term Persian was omitted, leaving only “The Gulf” (e.g., The Times Atlas, p. 39), while the historical term Persian Gulf mostly remained intact, as in the National Geographic Atlas (p. 77;
- ^Picture of Gamal Abdel Nasser’s handwritten letter, using the term Persian Gulf
- ^Picture of 1952 Saudi Arabian ARAMCO map using the name Persian Gulf
- ^Gerard Mercator Terrestrial globe, Arabian section (۱۵۴۱) via harvard.edu
- ^Gerard Mercator Mercator Projection world map (۱۵۶۹) via wilhelmkruecken.de
- ^Abraham Ortelius Map of Turkish Empire (۱۵۷۰) via cartographicarts.com
- ^Republic of Turkey Ministry of Culture and Tourism history pagekultur.gov.tr
- ^United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names Historical, Geographical and Legal Validity of the name ‘Persian Gulf’ (April 2006).
- ^[۱],Documents on the Persian Gulf’s name : the eternal heritage of ancient time Author: Ajam, Muḥammad.Pirouz Mojtahedzadeh retrieved 24 Feb. 2012.
- ^[۲],Conspiracy to change a heritage name: “The Persian Gulf”2002 by M.Ajam, retrieved 24 Feb. 2012.
- ^[۳],Documents on the Persian Gulf’s name : the eternal heritage of ancient time Author: Ajam, Muḥammad.Pirouz Mojtahedzadeh retrieved 24 Feb. 2012.
- ^“UN Editorial directive regarding the Persian Gulf“.
- ^“USE OF THE TERM “PERSIAN GULF”” (PDF).
- ^“Use of the terms “Persian Gulf”, “Gulf” and “Shatt al-Arab”” (PDF).f
- ^Report of the United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names on the work of its twenty-third session. Document E/2006/57, Economic and Social Council, United Nations. New York, 2006.[4]
- ^“Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd edition”. International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. Retrieved 6 February 2010.
- ^“Name game stokes U.S.-Iranian tensions – CNN.com”. CNN. 24 January 2008. Retrieved 22 May 2010.
- ^No Operation
- ^Spencer, Richard (23 February 2010). “Iran threatens flight ban over ‘Persian’ Gulf name row”. The Daily Telegraph (London). Retrieved 22 May 2010.
- ^[۵],IRIB,
- Arabian documents on the persian gulf:
http://www.youtube.com/user/IRANgulf1?feature=plcp - ‘arab’s documents on the persian gulf
- صدای جمال عبدالناصر در کاربرد خلیج فارسدر یوتیوب
- فیلم کامل مستنداسناد نام خلیج فارس[۳۲]
- فیلم مستند
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=meMsCEpBklc&list=FLDmuwcPepq735eIc-E1EvqQ
http://www.youtube.com/user/IRANgulf1?feature=watch
Occasional Paper by MEI
MEI is a forward looking, policy oriented non-governmental research institution, striving for academic openness. United Nations*
The Persian Gulf: Historical, Geographical and Legal Validity of the Name By: United Nations, is reproduced in Issue No. 22 ,Monday, 29 November 2010 by MEI
[Note: In recent years the historic nomenclature ‘Persian Gulf’ has been contested by the Arab countries which at times denote this region as Arabian Gulf.
In the light of this, some have settled for an unhistorical non-prefixed ‘Gulf’ to denote the body of water between the Arabian Peninsula and Iran.
In the light of the controversy, the 2006 UN report prepared by a panel of experts regarding the nomenclature is reproduced here as an Occasional Paper. Editor, MEI OP.]

No comments:
Post a Comment